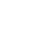
Edge Chipping Resistance Using Macroindentation
The resistance of the edges of brittle materials to chipping or flaking from concentrated loads is a critical property for dental restoration ceramics, resin composites, edge-mounted optical devices, ceramic tool bits, thin semiconductor chips, and many other materials. The edge chipping resistance test provides a method to quantify and measure the fracture resistance, toughness, and edge chip strength of these materials. This method uses a conical indenter to chip the rectangular edge of a brittle sample at set distances from the edge. Archeological evidence has revealed that this method is similar to the way early humans selected stones to make tools and weapons. Hundreds of thousands of years later, edge chipping tests remain a critical tool for applications where edge toughness is concerned.

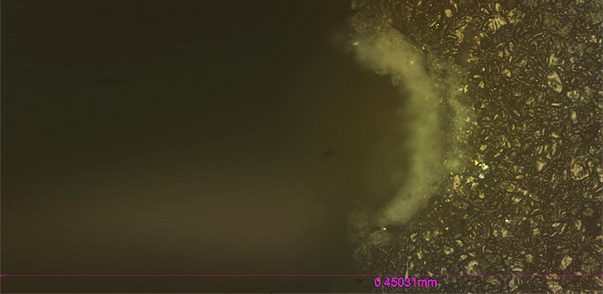
Rotational Measurement Using 3D Profilometry
Surface roughness and texture of the mechanical parts is vital to its end use. Conventional surface profilometry usually scan the sample surface from just one direction. A precise 360° rotational measurement of parts with a cylindrical shape is in need to measure detailed surface feature from different angles. Such 360° 3D inspection ensures the narrowest tolerances in quality control of manufacturing processes. Moreover, during the service time, wear creates dents, cracks, and surface roughening all over the cylindrical part surface. Surface inspection on one face of the sample may miss important information hidden on the backside.
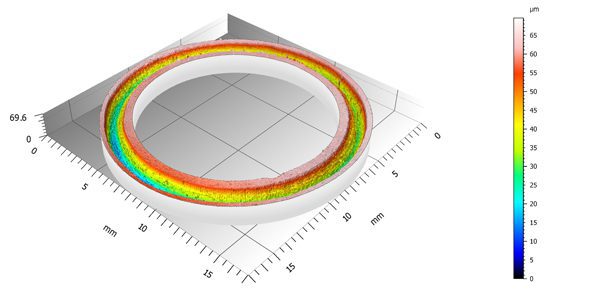
3D Wear Track Scan In Situ on Tribometer
Conventional pin-on-disc or reciprocating tribometer records the COF during the wear test. The wear rate is measured after the wear test by moving the sample to a profilometer and scanning the cross section profiles of the wear track. Such a method may introduce errors when the sample possesses an inhomogeneous wear track. Moreover, samples like multilayer coatings possess different wear resistance at different layers of the coating. A more reliable and repeatable technique for wear evaluation is in need – Nanovea developed a tribometer equipped with a 3D non-contact profilometer that performs a 3D scan of the complete wear track on the sample stage of the tribometer. It monitors the evolution of the 3D wear track morphology, allowing users to accurately calculate the wear rate and determine the failure mode at different stages using one test sample.
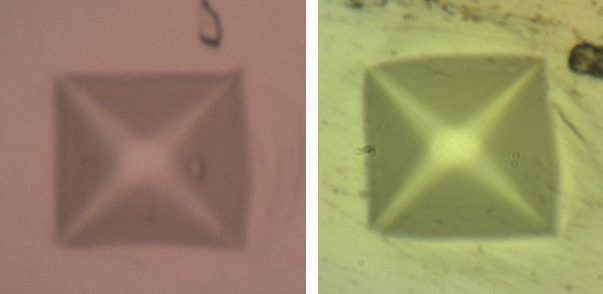
Low Load Vickers Hardness Measurement
During Vickers Hardness inevitable user errors are introduced during the measurement of the imprint under the microscope. Especially at low loads, small measurement errors of the indent size will produce large hardness deviations. In comparison, nanoindentation testing evaluates the mechanical properties of a material by driving the indenter tip into the test material and precisely recording the evolution of load and displacement of the tip. It avoids user errors in imprint size measurement.

Low Temperature Tribology
A reliable measurement of low temperature tribology, static and dynamic coefficient of friction, COF, as well as wear behavior is needed in order to better understand the tribological performance of materials for sub-zero applications. It provides a useful tool to correlate the frictional property with the influence of various factors, such as reactions at the interface, interlocking surface features, cohesion of surface films, and even microscopic solid static junctions between surfaces at low temperatures.
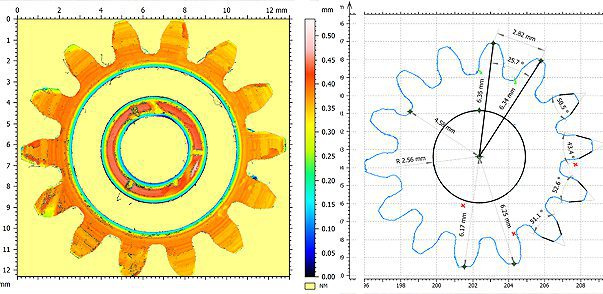
Gear Contour Analysis
Manufacturing of high precision gears requires stringent quality control, in order to obtain the best operational conditions and energy efficiency. Surface defects on the gears may lead to negative impact on the gear mesh quality. Moreover, during the service time, wear and tear takes places, creating surface defects such as dents and cracks in the gears that may result in decreased power transmission efficiency and potential mechanical failure. An accurate and quantifiable tool for surface inspection is in need. Unlike a touch probe technique, the Nanovea Profilometer performs 3D contour analysis of the sample without touching, making it possible to precisely scan samples with a complex shape, such as gears of different geometry.

Macro Adhesion Failure of DLC
bits and bearings. Under such extreme conditions, sufficient cohesive and adhesive strength of the coating/substrate system becomes vital. In order to select the best metal substrate for the target application and to establish a consistent coating process for DLC, it is critical to develop a reliable technique to quantitatively assess cohesion and adhesion failure of different DLC coating systems.
Cohesive & Adhesive Strength of DLC Using Macro Scratch Testing
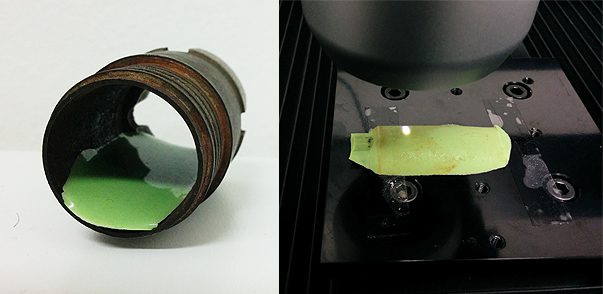
Replica Molding of Inner Pipe Corrosion
Surface finish of the metal pipe is critical for its product quality and performance. Rust progressively builds up and pits initiate and grow on the metal surface as corrosion process takes place, resulting in roughening of the pipe surface. The differential galvanic properties between metals, the ionic influences of solutions as well as the solution pH may all play roles in the pipe corrosion process, leading to corroded metal with different surface features. An accurate surface roughness and texture measurement of the corroded surface provides insight in the mechanisms involved in a specific corrosion process. Conventional profilometers have difficulty in reaching in and measuring the corroded inner pipe wall. Replica molding provides a solution by replicating the inner surface features in a non-destructive way. It can easily be applied on the inner wall of the corroded pipe and sets in 15 min. We scan the replicated surface of the replica molding to obtain the surface morphology of the inner pipe wall.

Corrosion Resistance of Coating After Scratch Testing
The corrosion resistant coatings should possess sufficient mechanical strength as they are often exposed to abrasive and erosive application environments. For example, the abrasive oil sands constantly wear away the inside of pipe, which progressively compromise the pipe’s integrity and potentially result in failure. In auto industry, corrosion takes place at the location of scratches on the auto
paint, especially during freezing winter when salts are applied on road. Therefore, a quantitative and reliable tool for measuring the
influence of scratch testing on protective coatings and its corrosion resistance is in need, in order to select the most proper coating for the intended application.

Nanovea Asia Visit 2016
Nanovea has just finished a successful seminar tour throughout Japan and is now currently meeting throughout China. We would like to thank our distributors and existing/potential clients for their time and hospitality.