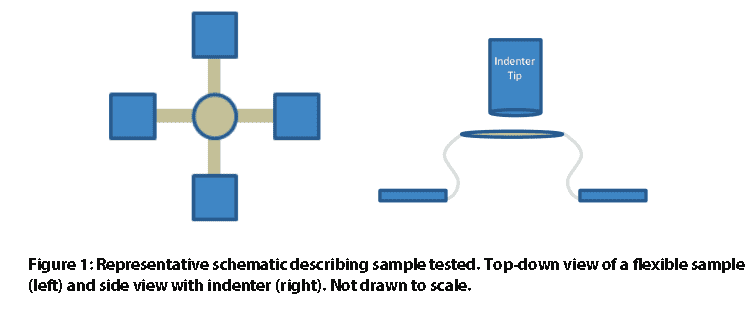
Monthly Archives: April 2019

Compression on Soft, Flexible Materials
Importance of testing soft, flexible materials
An example of very soft and flexible samples is a microelectromechanical system. MEMS are used in everyday commercial products like printers, mobile phones, and cars [1]. Their uses also include special functions, such as biosensors [2] and energy harvesting [3]. For their applications, MEMS must be able to reversibly transition between their original configuration to a compressed configuration repeatedly [4]. To understand how the structures will react to mechanical forces, compression testing can be conducted. Compression testing can be utilized to test and tune various MEMS configurations as well as testing upper and lower force limits for these samples.
Measurement Objective
In this case study, Nanovea conducted compression testing on two uniquely di erent flexible, spring-like samples. We showcase our ability to conduct compression at very low loads and record large displacement while accurately obtaining data at low loads and how this can be applied to the MEMS industry. Due to privacy policies, the samples and their origin will not be revealed in this study
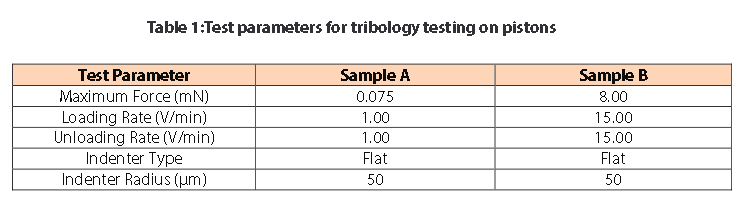
Measurement Parameters
Note: The loading rate of 1 V/min is proportional to approximately 100μm of displacement when the indenter is in the air.
Results and Discussion
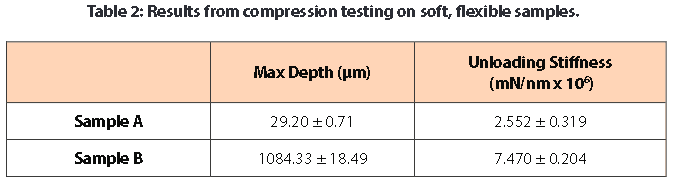
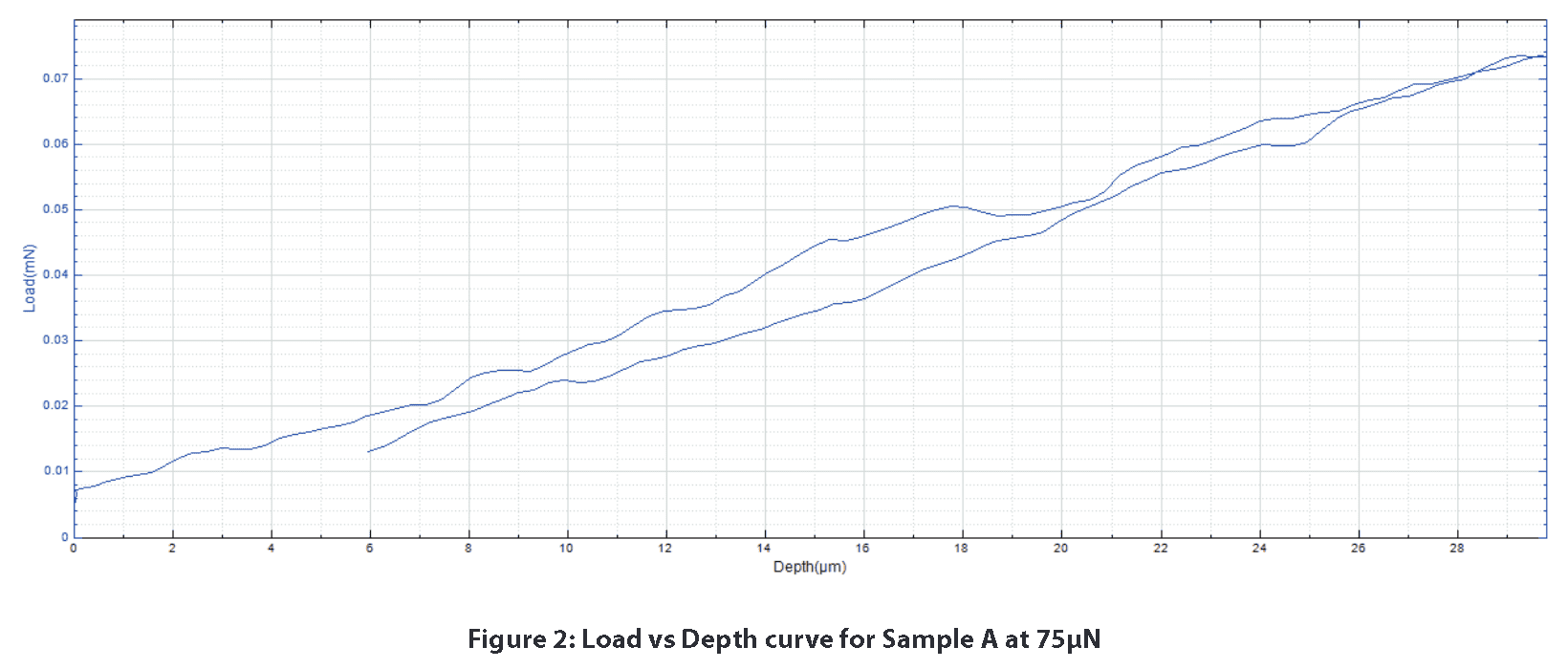
The sample’s response to mechanical forces can be seen in the load vs depth curves. Sample A only displays linear elastic deformation with the test parameters listed above. Figure 2 is a great example of the stability that can be achieved for a load vs. depth curve at 75μN. Due to the load and depth sensors stability, it would be easy to perceive any signi cant mechanical response from the sample.
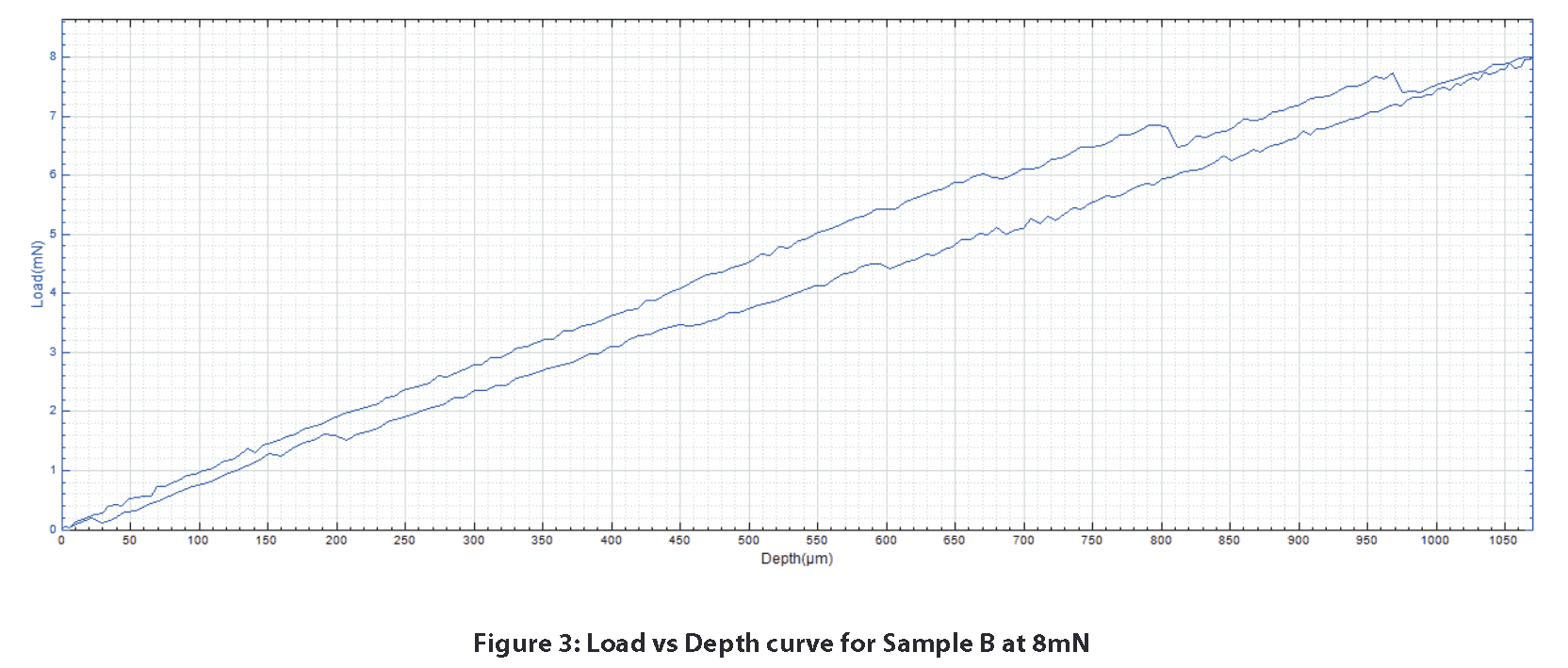
Sample B displays a different mechanical response from Sample A. Past 750μm of depth, fracture-like behavior in the graph begins to appear. This is seen with the sharp drops in load at 850 and 975μm of depth. Despite traveling at a high loading rate for more than 1mm over a range of 8mN, our highly sensitive load and depth sensors allow the user to obtain the sleek load vs depth curves below.
The stiffness was calculated from the unloading portion of the load vs depth curves. Stiffness reflects how much force is necessary to deform the sample. For this stiffness calculation, a pseudo Poisson’s ratio of 0.3 was used since the actual ratio of the material is not known. In this case, Sample B proved to be stiffer than Sample A.
Conclusion
Two diff erent flexible samples were tested under compression using the Nanovea Mechanical Tester’s Nano Module. The tests were conducted at very low loads (<80μN) and over a large depth range (>1mm). Nano-scaled compression testing with the Nano Module has shown the module’s ability to test very soft and flexible samples. Additional testing for this study could address how repeated cyclical loading a ects the elastic recovery aspect of the spring-like samples via the Nanovea Mechanical Tester’s multi-loading option.
For more information on this testing method, feel free to contact us at [email protected] and for additional application notes please browse our extensive Application Note digital library.
References
[1] “Introduction and Application Areas for MEMS.” EEHerald, 1 Mar. 2017, www.eeherald.com/section/design-guide/mems_application_introduction.html.
[2] Louizos, Louizos-Alexandros; Athanasopoulos, Panagiotis G.; Varty, Kevin (2012). “Microelectromechanical Systems and Nanotechnology. A Platform for the Next Stent Technological Era”. Vasc Endovascular Surg.46 (8): 605–609. doi:10.1177/1538574412462637. PMID 23047818.
[3] Hajati, Arman; Sang-Gook Kim (2011). “Ultra-wide bandwidth piezoelectric energy harvesting”. AppliedPhysics Letters. 99 (8): 083105. doi:10.1063/1.3629551.
[4] Fu, Haoran, et al. “Morphable 3D mesostructures and microelectronic devices by multistable bucklingmechanics.” Nature materials 17.3 (2018): 268.
NOW, LET'S TALK ABOUT YOUR APPLICATION

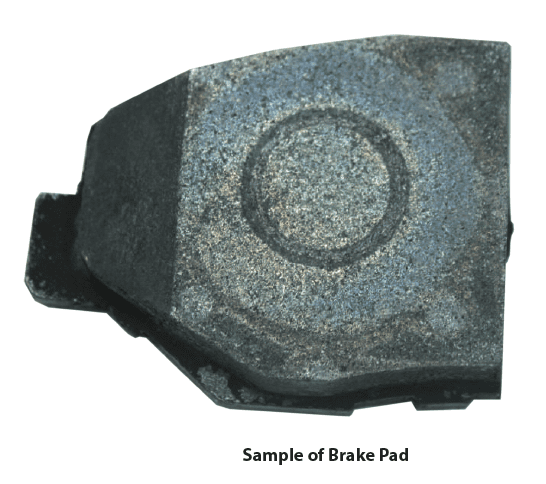
Evaluating Brake Pads with Tribology
Importance of Evaluating Break Pad Performance
Brake pads are composites., a material made up of multiple ingredients, that must be able to satisfy a large number of safety requirements. Ideal brake pads have high coefficient of friction (COF), low wear rate, minimal noise, and remain reliable under varying environments. To ensure the quality of brake pads are able to satisfy their requirements, tribology testing can be used to identify critical specifications.
The importance of the reliability of brake pads is placed very high; the safety of passengers should never be neglected. Therefore, it is key to replicate operating conditions and identify possible points of failure.
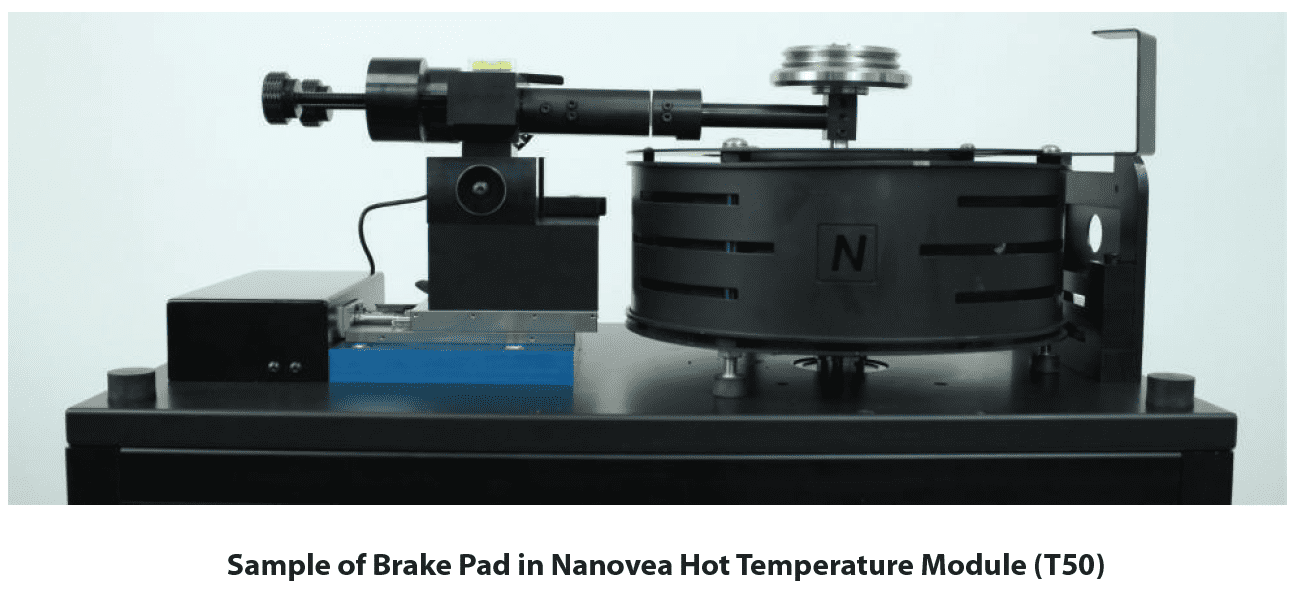
With the Nanovea Tribometer, a constant load is applied between a pin, ball, or flat and a constantly moving counter material. The friction between the two material is collected with a stiff load cell, allowing the collection of material properties at different loads and speeds and tested in high temperature, corrosive, or liquid environments.
Measurement Objective
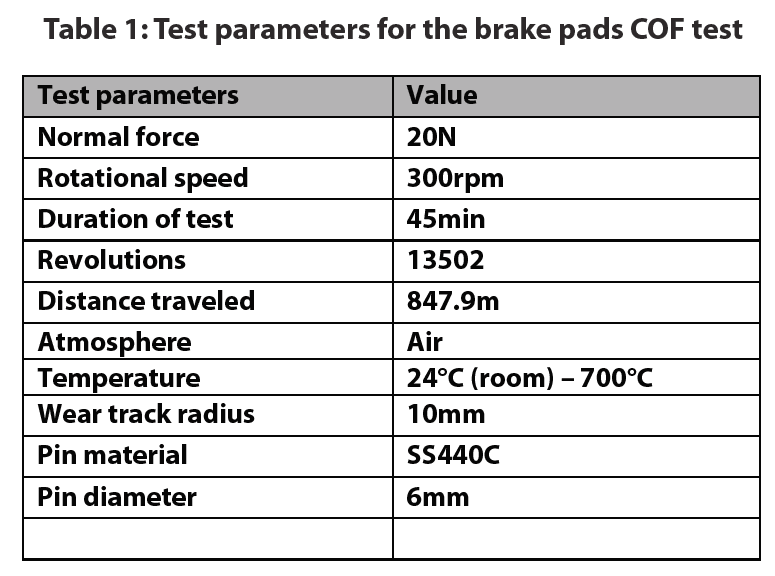
In this study, the coefficient of friction of the brake pads were studied under a continuously increasing temperature environment from room temperature to 700°C. The environmental temperature was raised in-situ until noticeable failure of the brake pad was observed. A thermocouple was attached to the backside of the pin to measure the temperature near the sliding interface.
Results and Discussion
This study focuses mainly on the temperature at which brake pads start to fail. The COF obtained do not represent real-life values; the pin material is not the same as brake rotors. It should also be noted that the temperature data collected is the temperature of the pin and not the sliding interface temperature
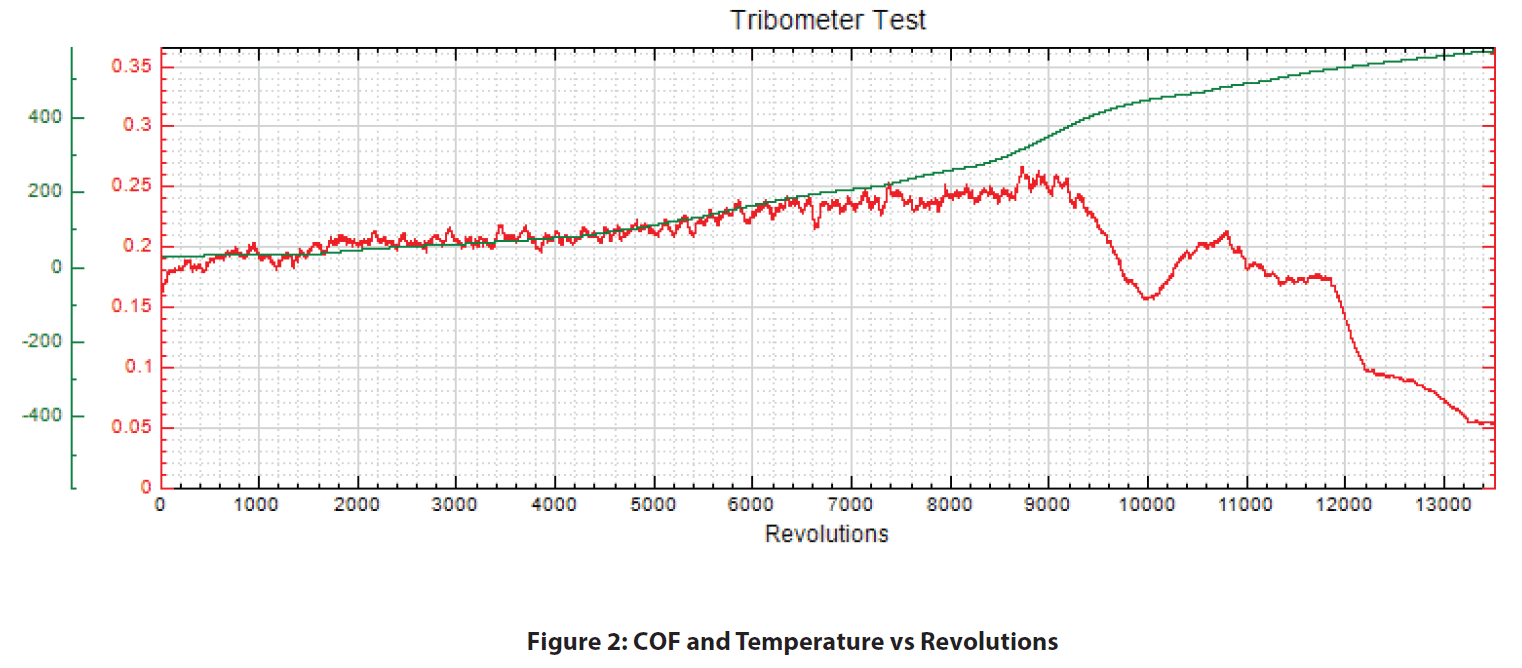
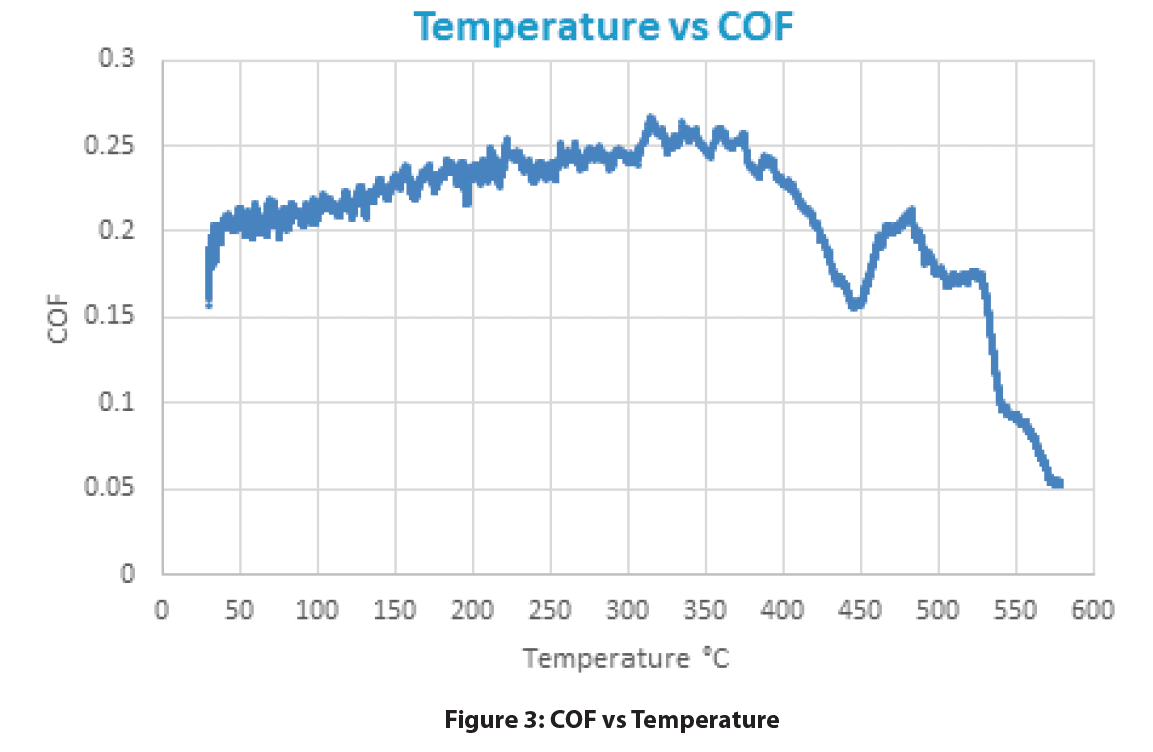
At the start of the test (room temperature), the COF between the SS440C pin and brake pad gave a consistent value of approximately 0.2. As the temperature increased, the COF steadily increased and peaked at a value of 0.26 near 350°C. Past 390°C, the COF quickly starts decreasing. The COF began to increase back to 0.2 at 450°C but starts decreasing to a value of 0.05 shortly after.
The temperature at which the brake pads consistently failed is identified at temperatures above 500°C. Past this temperature, the COF was no longer able to retain the starting COF of 0.2.
Conclusion

The brake pads have shown consistent failure at a temperature past 500°C. Its COF of 0.2 slowly rises to a value of 0.26 before dropping down to 0.05 at the end of the test (580°C). The difference between 0.05 and 0.2 is a factor of 4. This means that the normal force at 580°C must be four times greater than at room temperature to achieve the same stopping force!
While not included in this study, the Nanovea Tribometer is also able to conduct testing to observe another important property of brake pads: wear rate. By utilizing our 3D non-contact profilometers, the volume of the wear track can be obtained to calculate how quickly samples wear. Wear testing can be conducted with the Nanovea Tribometer under different test conditions and environments to best simulate operating conditions.
NOW, LET'S TALK ABOUT YOUR APPLICATION
Quality Analysis on Electrical Discharge Machined Metals
Electrical discharge machining, or EDM, is a manufacturing process that removes material via electrical
discharges [1]. This machining process is generally used with conductive metals that would be difficult
to machine with conventional methods.
As with all machining processes, precision and accuracy must be high in order to meet acceptable
tolerance levels. In this application note, the quality of the machined metals will be assessed with a
Nanovea 3D non-contact profilometer.
Categories
- Application Notes
- Block on Ring Tribology
- Corrosion Tribology
- Friction Testing | Coefficient of Friction
- High Temperature Mechanical Testing
- High Temperature Tribology
- Humidity and Gases Tribology
- Humidity Mechanical Testing
- Indentation | Creep and Relaxation
- Indentation | Fracture Toughness
- Indentation | Hardness and Elastic
- Indentation | Loss and Storage
- Indentation | Stress vs Strain
- Indentation | Yield Strength and Fatigue
- Laboratory Testing
- Linear Tribology
- Liquid Mechanical Testing
- Liquid Tribology
- Low Temperature Tribology
- Mechanical Testing
- Press Release
- Profilometry | Flatness and Warpage
- Profilometry | Geometry and Shape
- Profilometry | Roughness and Finish
- Profilometry | Step Height and Thickness
- Profilometry | Texture and Grain
- Profilometry | Volume and Area
- Profilometry Testing
- Ring on Ring Tribology
- Rotational Tribology
- Scratch Testing | Adhesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Cohesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Multi-Pass Wear
- Scratch Testing | Scratch Hardness
- Scratch Testing Tribology
- Tradeshow
- Tribology Testing
- Uncategorized
Archives
- September 2023
- August 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- July 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- October 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- November 2010
- January 2010
- April 2009
- March 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- October 2008
- August 2007
- July 2006
- March 2006
- January 2005
- April 2004