Category: Uncategorized
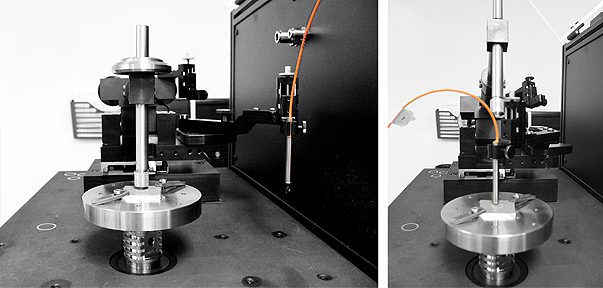
In Situ Measurement Of Wear Rate Evolution
Nanovea has introduced a new highly accurate and cost effective solution to evaluate wear rate in situ on the Tribometer equipped with a 2d Non-Contact Profilometer (ASTM G99 or G133). Wear rate evolution as a function of testing time can now be plotted in record time using a single sample.
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nano scratch testing of PTFE coated wires
• Nanoindentation of thin gold plated micro features
• Micro scratch of anodized titanium
• Micro wear of anodized titanium

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Flatness of a metal seal
• Dimension of Intraocular lenses
• Volume loss measurement of corroded aluminum
• Topography patterns of non woven fabric

Tribology:
• Characterization of “stick & slip” phenomenon on rubber samples
• Wear testing of DLC coatings
• Friction testing lubrication samples
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation puncture of film
• Nanoindentation compression of micro features
• Nanofriction in liquid of medical lead
• Microindentation hardness testing of rock
• Microscratch of dlc coatings
• Microscratch of commercial coating

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Roughness of micro machined parts
• Texture of fabric
• Finish “Orange Peel” of coatings
• Topography of corroded steel
• Flatness of gold plated wafers

Tribology:
• Wear testing of dlc coatings
• Wear testing ptfe coatings

CUSTOM BOTTLE ON BOTTLE FRICTION TEST
This month Nanovea is proud to highlight the endless possible configurations of the Mechanical Tester. Seen above, is a custom glass bottle-on-bottle sample holder for precise load controlled bottle friction test using the Macro Module.
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation of dma of soft polymer
• Nanoscratch of fused dielectric films
• Nanowear of polymer coatings
• Microindentation of gas nitride steel
• Microscratch of sapphire coatings

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Roughness of machined parts
• Finish of hard dog food biscuits
• Flatness of micro squares
• Profile of biomedical pouch seals
• Dimensions of machined parts
• Wear testing of sapphire coating
• Wear testing of frangible bullets
• Friction testing of hard dog biscuits
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation of antireflective coatings
• Nanoindentation of biomedical gels
• Nanoscratch of fused silica and silicon
• Nanofriction of micro rubber stoppers
• Microscratch of anodized titanium

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Roughness of thermal coatings
• Finish of hip implant
• Flatness & Planarity of electrical contacts
• Shape and Form of stamped sheet metal patterns
• Dimensions of molded plastic lenses

Tribology:
• Wear testing of tool steel grip pads
• High temperature wear testing of ceramics
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation of wire cross sections
• Nanoindentation of Y2O3 thin films
• Nanoscratch of thin polymer films
• Nanoscratch of catheters
• Microindentation of oil-well cement

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Roughness of catheters
• Finish of processed leather
• Topography of thin film particle contaminants
• Coplanarity of ball grid arrays
• Step height of microchannels
• Stribeck Curve evaluation of various lubrication
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation of nickel coatings
• Nanoindentation compression of adhesive
• Nanoscratch of ceramic coatings
• Microindentation of seawater aged rubber
• Microscratch of anodized coatings

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Leather roughness measurement
• Form consistency of stamped metal
• Topography consistency of woven fabric
• Texture of molded plastic surfaces
• Depth of extrusion die pits

Tribology:
• Wear rate of Ti-MoS2 and WC coatings in dry, liquid and high temp conditions
Here are examples of materials we tested this month:

Mechanical:
• Nanoindentation mapping of micro parts
• Nanoindentation fracture of ceramic samples
• Nano Scratch of coated glass
• Nano Scratch failure of implant coatings
• Macroindentation of anodized coatings
• Micro Scratch of acrylic urethane coatings
• Macro Scratch of rock samples

3D Non-Contact Profilometry:
• Roughness of micro channels
• Roughness of curved plastics
• Texture of micro emboss
• Finish of powder coatings
• Coplanarity of micro features
• Dimensions of micro parts

Tribology:
• Linear Wear Testing of engine parts
• Rotative Wear Testing of ceramic samples

COLLABORATION TO IMPROVE TABER ABRASION TESTING
Traditionally, Taber abrasion testing is carried out to evaluate the wear resistance of Industrial Coatings according to ASTM D4060 Standard. However, as mentioned in the ASTM D4060 standard, “For some materials, abrasion tests utilizing the Taber Abraser may be subject to variation due to changes in the abrasive characteristics of the wheel during testing.” This may result in poor reproducibility of test results and create difficulty in comparing values reported from different laboratories. Moreover, in Taber abrasion test, abrasion resistance is calculated as loss in weight at a specified number of abrasion cycles. However, for example acrylic urethane floor paints have a recommended dry film thickness of 37.5-50 μm. The aggressive abrasion process by Taber Abraser can quickly wear through the acrylic urethane coating and create mass loss to the substrate, which leads to substantial errors in the calculation of the paint weight loss. The implant of abrasive particles in the paint during the abrasion test also contributes to the errors. Therefore, a well-controlled quantifiable and reliable measurement is crucial to ensure reproducible wear evaluation; such as a Tribometer.
Learn more in this months app note: Industrial Coating Scratch & Wear Evaluation