INTRODUCTION
The combination of high hardness, excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance and inertness makes titanium nitride (TiN) an ideal protective coating for metal components in various industries. For example, the edge retention and corrosion resistance of a TiN coating can substantially increase the work efficiency and extend the service life of machine tooling such as razor blades, metal cutters, injection molds and saws. Its high hardness, inertness and non-toxicity make TiN a great candidate for applications in medical devices including implants and surgical instruments.
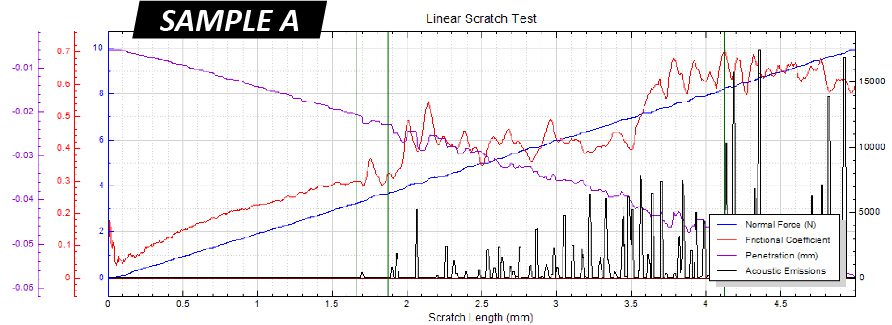
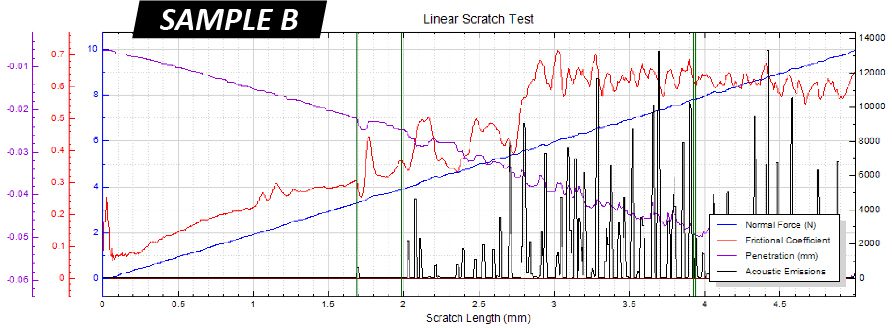
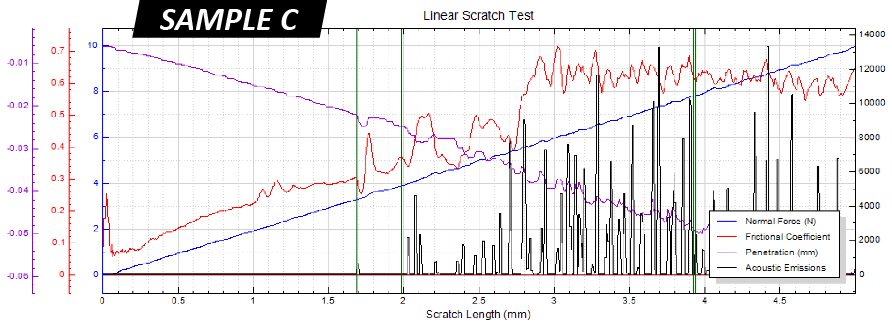
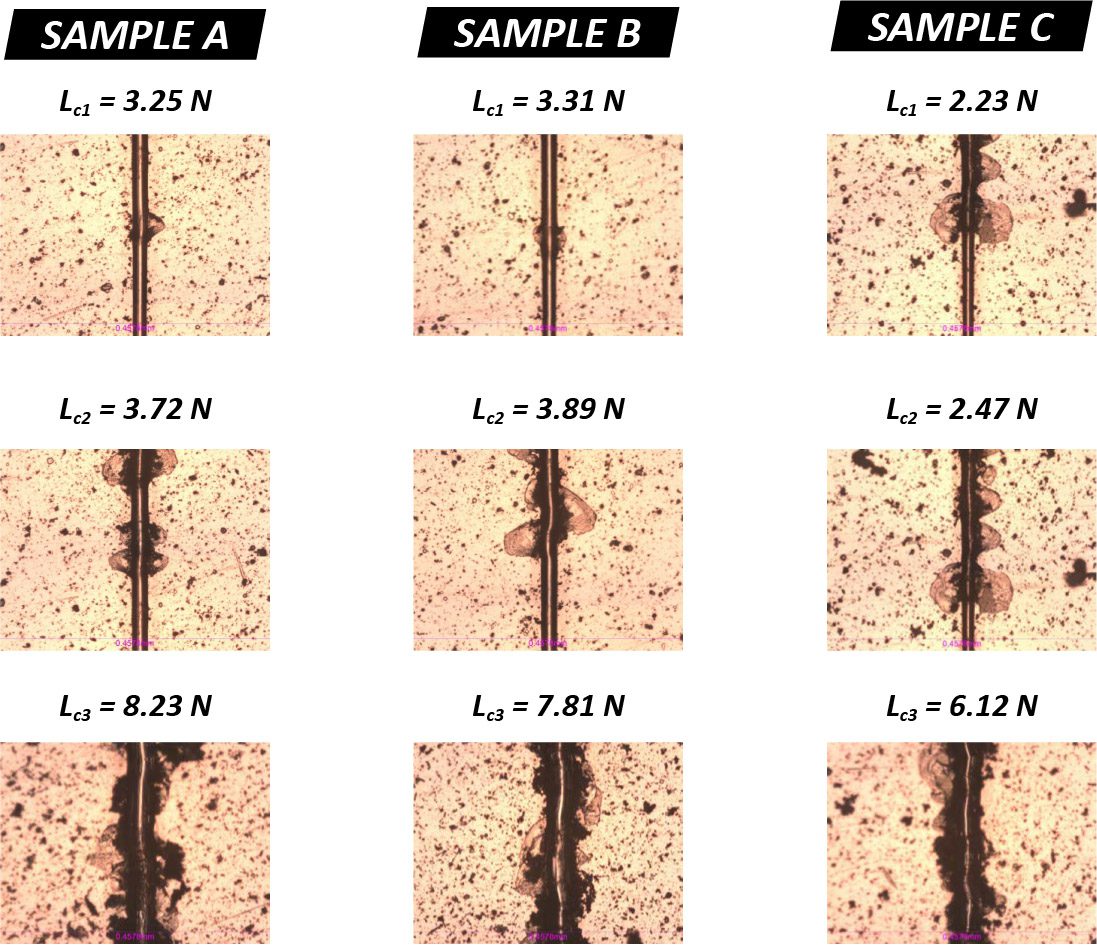
IMPORTANCE OF TiN COATING SCRATCH TESTING
Residual stress in protective PVD/CVD coatings plays a critical role in the performance and mechanical integrity of the coated component. The residual stress derives from several major sources, including growth stress, thermal gradients, geometric constraints and service stress¹. The thermal expansion mismatch between the coating and the substrate created during coating deposition at elevated temperatures leads to high thermal residual stress. Moreover, TiN coated tools are often used under very high concentrated stresses, e.g. drill bits and bearings. It is critical to developing a reliable quality control process to quantitatively inspect the cohesive and adhesive strength of protective functional coatings.
[1] V. Teixeira, Vacuum 64 (2002) 393–399.