Honeycomb Panel Surface Finish with 3D Profilometry
INTRODUCTION
Roughness, porosity, and texture of the honeycomb panel surface are critical to quantify for the final panel design. These surface qualities can directly correlate to the aesthetics and functional characteristics of the panel surface. A better understanding of the surface texture and porosity can help optimize the panel surface processing and manufacturability. A quantitative, precise, and reliable surface measurement of the honeycomb panel is needed to control surface parameters for application and painting requirements. The Nanovea 3D Non-Contact sensors utilize unique chromatic confocal technology capable of precisely measuring these panel surfaces.
MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE
In this study, the Nanovea HS2000 platform equipped with a high-speed Line Sensor was used to measure and compare two honeycomb panels with different surface finishes. We showcase the Nanovea non-contact profilometer’s ability to provide fast and precise 3D profiling measurements and comprehensive in-depth analysis of the surface finish.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
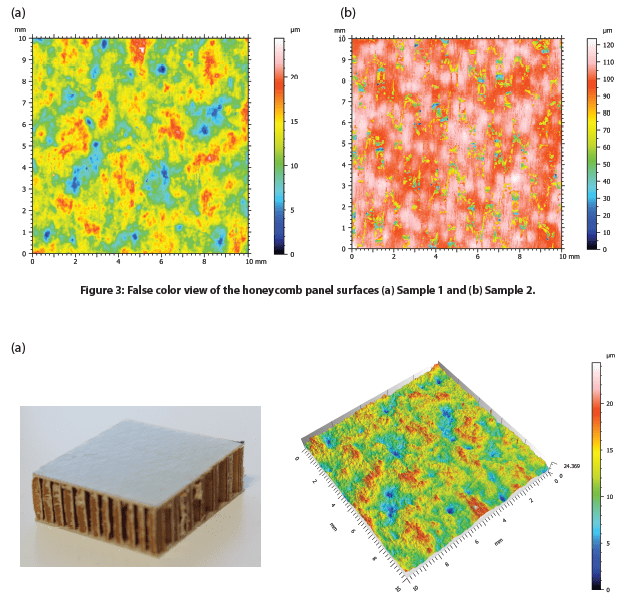
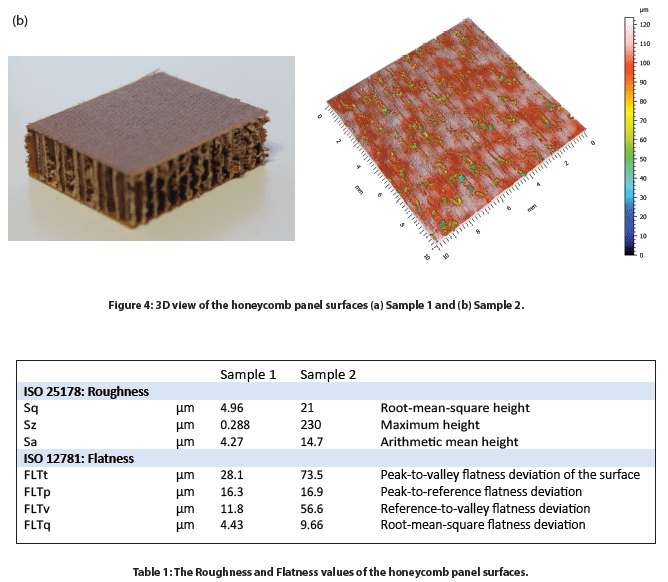
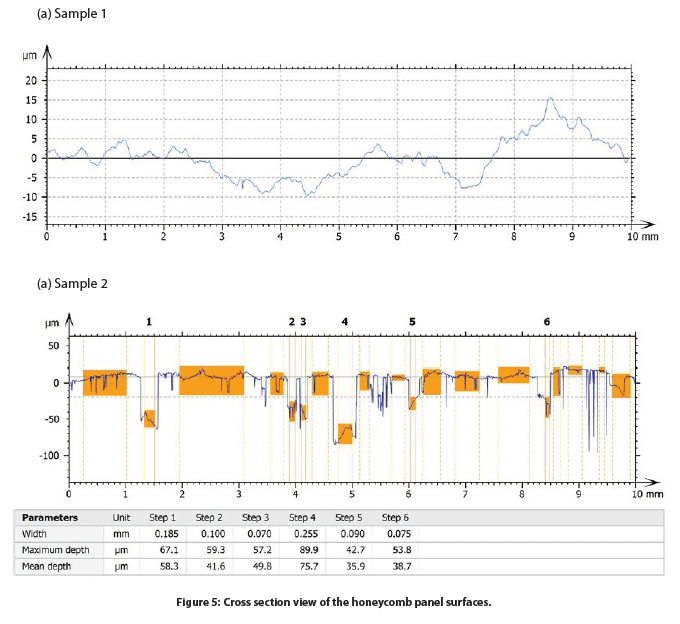
The surface of two honeycomb panel samples with varied surface finishes, namely Sample 1 and Sample 2, were measured. The false color and 3D view of the Samples 1 and 2 surfaces are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. The roughness and flatness values were calculated by advanced analysis software and are compared in Table 1. Sample 2 exhibits a more porous surface compared to Sample 1. As a result, Sample 2 possesses a higher roughness Sa of 14.7 µm, compared to an Sa value of 4.27 µm for Sample 1.
The 2D profiles of the honeycomb panel surfaces were compared in Figure 5, allowing users to have a visual comparison of the height change at different locations of the sample surface. We can observe that Sample 1 has a height variation of ~25 µm between the highest peak and lowest valley location. On the other hand, Sample 2 shows several deep pores across the 2D profile. The advanced analysis software has the ability to automatically locate and measure the depth of six relatively deep pores as shown in the table of Figure 4.b Sample 2. The deepest pore amongst the six possesses a maximum depth of nearly 90 µm (Step 4).
To further investigate the pore size and distribution of Sample 2, porosity evaluation was performed and discussed in the following section. The sliced view is displayed in Figure 5 and the results are summarized in Table 2. We can observe that the pores, marked in blue color in Figure 5, have a relatively homogeneous distribution on the sample surface. The projected area of the pores constitutes 18.9% of the whole sample surface. The volume per mm² of the total pores is ~0.06 mm³. The pores have an average depth of 42.2 µm, and the maximum depth is 108.1 µm.
CONCLUSION
In this application, we have showcased that the Nanovea HS2000 platform equipped with a high-speed Line Sensor is an ideal tool for analyzing and comparing the surface finish of honeycomb panel samples in a fast and accurate manner. The high-resolution profilometry scans paired with an advanced analysis software allow for a comprehensive and quantitative evaluation of the surface finish of honeycomb panel samples.
The data shown here represents only a small portion of the calculations available in the analysis software. Nanovea Profilometers measure virtually any surface for a wide range of applications in the Semiconductor, Microelectronic, Solar, Fiber Optics, Automotive, Aerospace, Metallurgy, Machining, Coatings, Pharmaceutical, Biomedical, Environmental and many other industries.
NOW, LET'S TALK ABOUT YOUR APPLICATION
Categories
- Application Notes
- Block on Ring Tribology
- Corrosion Tribology
- Friction Testing | Coefficient of Friction
- High Temperature Mechanical Testing
- High Temperature Tribology
- Humidity and Gases Tribology
- Humidity Mechanical Testing
- Indentation | Creep and Relaxation
- Indentation | Fracture Toughness
- Indentation | Hardness and Elastic
- Indentation | Loss and Storage
- Indentation | Stress vs Strain
- Indentation | Yield Strength and Fatigue
- Laboratory Testing
- Linear Tribology
- Liquid Mechanical Testing
- Liquid Tribology
- Low Temperature Tribology
- Mechanical Testing
- Press Release
- Profilometry | Flatness and Warpage
- Profilometry | Geometry and Shape
- Profilometry | Roughness and Finish
- Profilometry | Step Height and Thickness
- Profilometry | Texture and Grain
- Profilometry | Volume and Area
- Profilometry Testing
- Ring on Ring Tribology
- Rotational Tribology
- Scratch Testing | Adhesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Cohesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Multi-Pass Wear
- Scratch Testing | Scratch Hardness
- Scratch Testing Tribology
- Tribology Testing
- Uncategorized
Archives
- November 2025
- September 2023
- August 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- July 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- October 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- November 2010
- January 2010
- April 2009
- March 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- October 2008
- August 2007
- July 2006
- March 2006
- January 2005
- April 2004