Category: Scratch Testing | Adhesive Failure
Micro Scrape Test Of Polymeric Coating
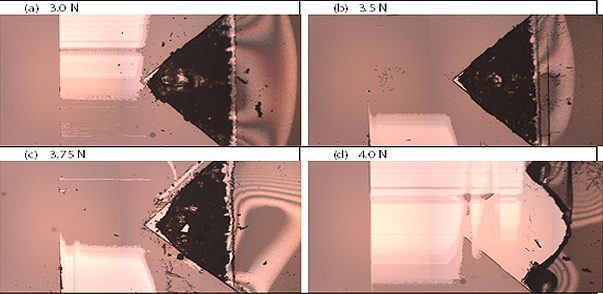
Scratch testing has developed to be one of the most widely applied methods to evaluate the cohesive and adhesive strength of the coatings. The critical load, at which a certain type of coating failure occurs as the applied load progressively increases, is widely regarded as a reliable tool to determine and compare the adhesive and cohesive properties of the coatings. The most commonly used indenter for scratch testing is the conical Rockwell diamond indenter. However, when the scratch test is performed on the soft polymeric coating deposited on a brittle substrate such as silicon wafer, the conical indenter tends to plough through the coating forming grooves rather than creating cracks or delamination. Cracking of the brittle silicon wafer takes place when the load further increases. Therefore, it is vital to develop a new technique to evaluate the cohesion or adhesion properties of soft coatings on a brittle substrate.

Grooved Stent Coating Failure Using Nano Scratch Testing
Drug–eluting stent is a novel approach in stent technology. It possesses a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer coating that releases medicine slowly and continuously at the local artery to inhibit intimal thickening and prevent the artery from being blocked again. One of the major concerns is the delamination of the polymer coating that carries the drug-eluting layer from the metal stent substrate. In order to improve the adhesion of this coating to the substrate, the stent is designed in different shapes. Specifically in this study, the polymer coating locates at the bottom of the groove on the mesh wire, which brings enormous challenge to the adhesion measurement. A reliable technique is in need to quantitatively measure the interfacial strength between the polymer coating and the metal substrate. The special shape and the small diameter of the stent mesh (comparable to a human hair) require ultrafine X-Y lateral accuracy to locate the test position and proper control and measurement of the load and depth during the test.

Macro Adhesion Failure of DLC
bits and bearings. Under such extreme conditions, sufficient cohesive and adhesive strength of the coating/substrate system becomes vital. In order to select the best metal substrate for the target application and to establish a consistent coating process for DLC, it is critical to develop a reliable technique to quantitatively assess cohesion and adhesion failure of different DLC coating systems.
Cohesive & Adhesive Strength of DLC Using Macro Scratch Testing

Gold Coating Adhesion on Quartz Crystal Substrate
As an extremely accurate device, the Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) measures the mass change down to 0.1 nanogram. Any mass loss or delamination of the electrodes on the quartz plate will be detected by the quartz crystal and cause significant measurement errors. As a result, the intrinsic quality of the electrode gold coating and the interfacial integrity of the coating/substrate system play an essential role in performing accurate and repeatable mass measurement. The Micro scratch test is a widely used comparative measurement to evaluate the relative cohesion or adhesion properties of coatings based on comparison of the critical loads at which failures appear. It is a superior tool for reliable quality control of QCMs.