Category: High Temperature Mechanical Testing

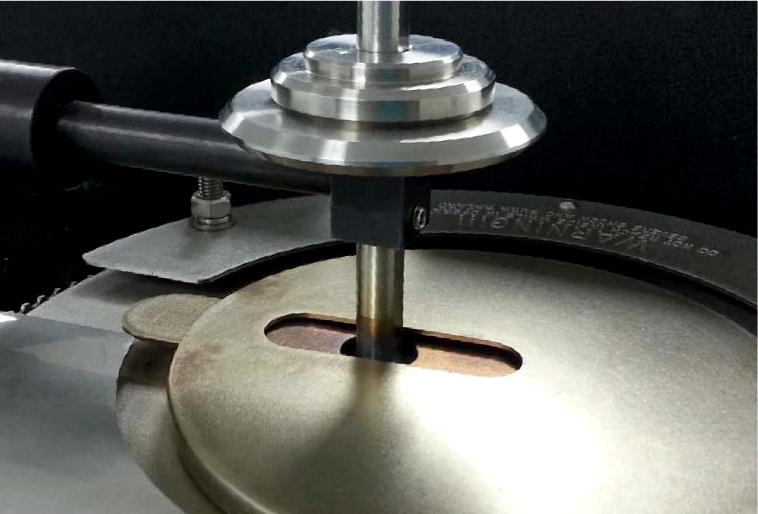
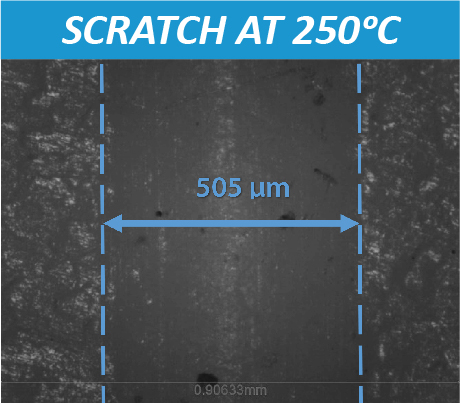
High Temperature Scratch Hardness using a Tribometer
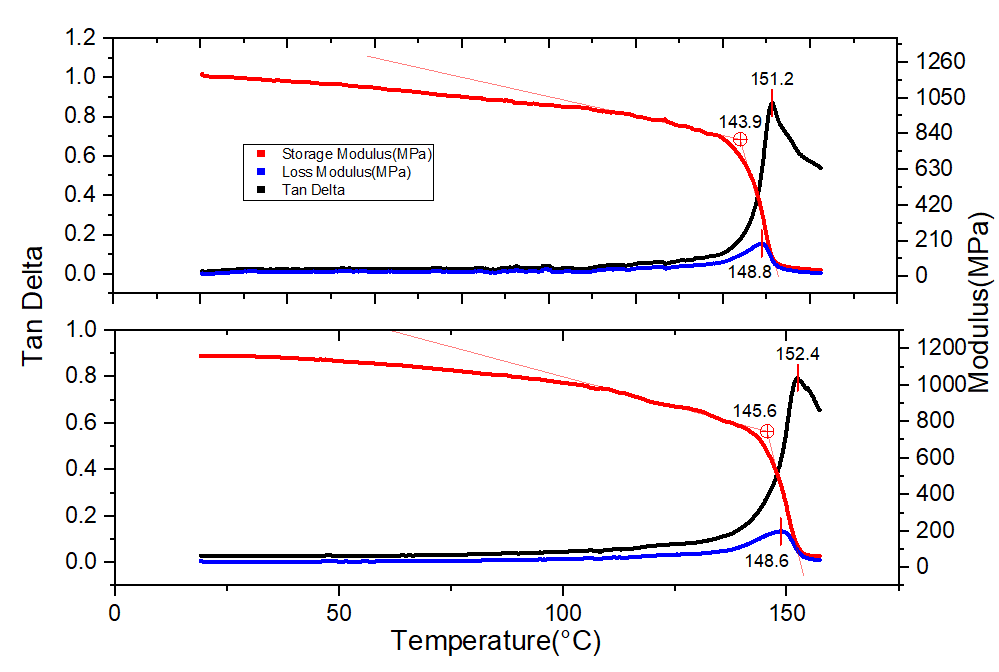
Precise Localized Glass Transition with Nanoindentation DMA

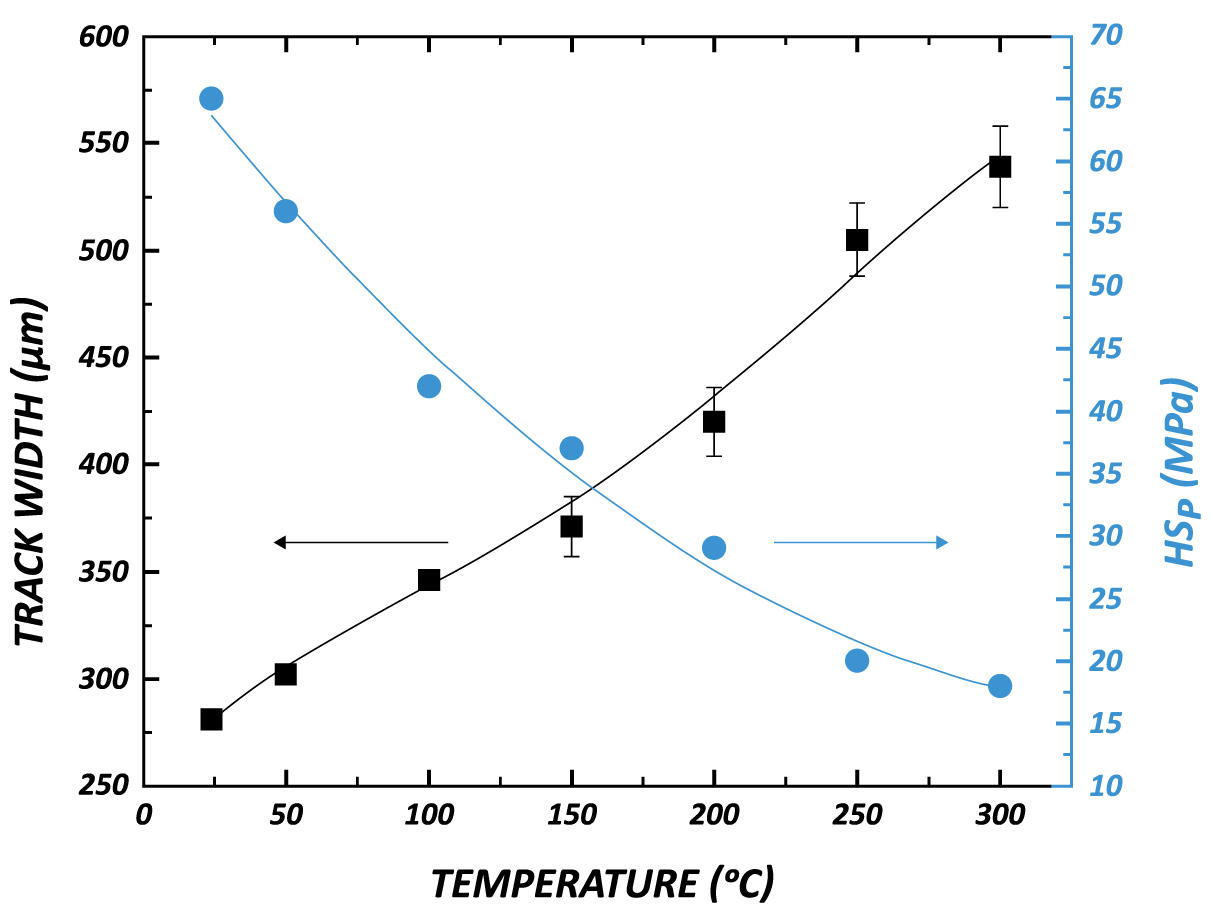
ASTM D7187 Temperature Effect Using Nanoscratching
ASTM D7187, the resistance of the paint to scratch and mar plays a vital role in its end use. Automotive paint susceptible to scratches makes it difficult and costly to maintain and repair. Different coating architectures of the primer, basecoat, and clearcoat have been developed to achieve the best scratch/mar resistance. Nanoscratch testing has been developed as a standard test method to measure the mechanistic aspects of scratch/mar behavior of paint coatings as described in ASTM D7187. Different elementary deformation mechanisms, namely elastic deformation, plastic deformation and fracture, occur at different loads during the scratch test. It provides a quantitative assessment of the plastic resistance and fracture resistance of the paint coatings.
ASTM D7187 Temperature Effect Using Nanoscratching

Teflon Mechanical Properties at High Temperature
At elevated temperatures, heat changes teflon mechanical properties such as the hardness and viscoelasticity, which may result in mechanical failures. A reliable measurement of the thermo-mechanical behavior of polymeric materials is in need to quantitatively evaluate the candidate materials for high temperature applications. The Nano module of the Nanovea Mechanical Tester studies the Hardness, Young’s Modulus and Creep by applying the load with a high-precision piezo and measuring the evolution of force and displacement. An advanced oven creates a uniform temperature surrounding the indentation tip and the sample surface throughout the nanoindentation test so as to minimize the effect of thermal drift.
Teflon Mechanical Properties at High Temperature Using Nanoindentation
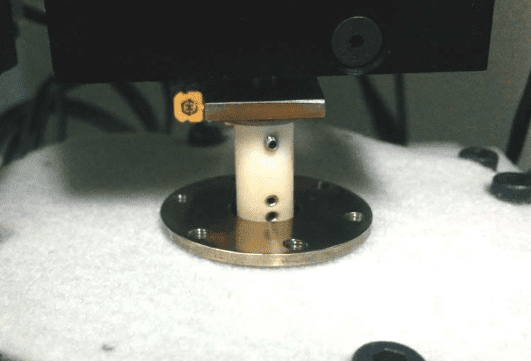
Thermomechanical Analysis of Solder Using Nanoindentation
Solder joints are subjected to thermal and/or external stress when the temperature exceeds 0.6 Tm where Tm is the melting point of the material in Kelvin. The creep behavior of solders at elevated temperatures can directly influence the reliability of solder interconnections. As a result, a reliable and quantitative thermomechanical analysis of the solder at different temperatures is in need. The Nano module of the Nanovea Mechanical Tester applies the load by a high-precision piezo and directly measures the evolution of force and displacement. The advanced heating oven provides a uniform temperature at the tip and sample surface, which ensures measuring accuracy and minimizes the influence of thermal drift.
Thermomechanical Analysis of Solder Using Nanoindentation

High Temperature Scratch Hardness Using Tribometer
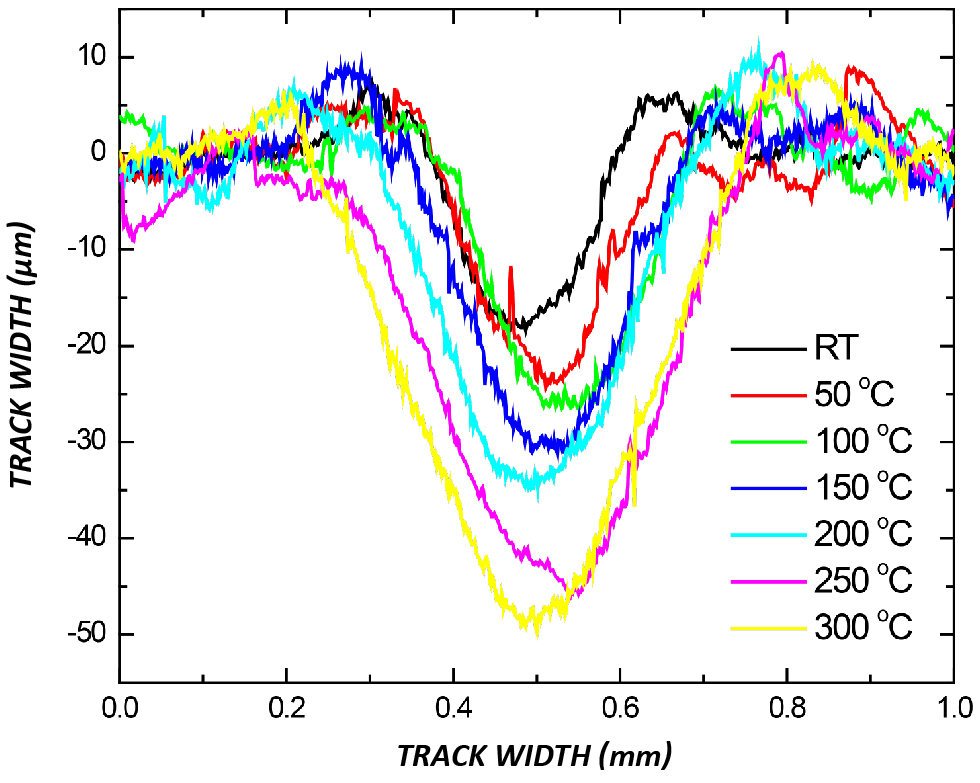
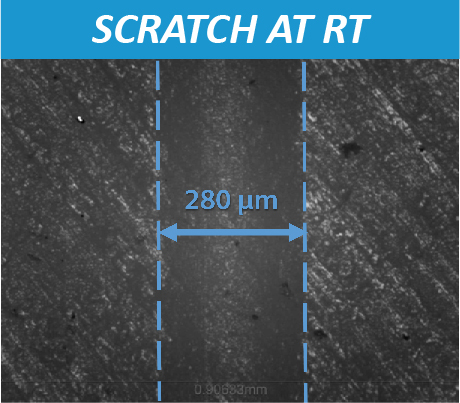
Materials are selected based on the service requirements. For applications involving significant temperature changes and thermal gradients, it is critical to investigate the mechanical properties of materials at high temperatures to be fully aware of the mechanical limits. Materials, especially polymers, usually soften at high temperatures. A lot of mechanical failures are caused by creep deformation and thermal fatigue taking place only at elevated temperatures. Therefore, a reliable technique for measuring high temperature scratch hardness is in need to ensure proper selection of the materials for high temperature applications.
High Temperature Scratch Hardness Using Tribometer