Wear and Scratch Evaluation of Surface Treated Copper Wire
Importance of Wear and Scratch Evaluation of Copper Wire
Copper has a long history of use in electric wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and telegraph. Copper wires are applied in a wide range of electronic equipment such as panels, meters, computers, business machines, and appliances thanks to its corrosion resistance, solderability, and performance at elevated temperatures up to 150°C. Approximately half of all mined copper is used for manufacturing electrical wire and cable conductors.
Copper wire surface quality is critical to application service performance and lifetime. Micro defects in wires may lead to excessive wear, crack initiation and propagation, decreased conductivity, and inadequate solderability. Proper surface treatment of copper wires removes surface defects generated during wire drawing improving corrosion, scratch, and wear resistance. Many aerospace applications with copper wires require controlled behavior to prevent unexpected equipment failure. Quantifiable and reliable measurements are needed to properly evaluate the wear and scratch resistance of the copper wire surface.
Measurement Objective
In this application we simulate a controlled wear process of different copper wire surface treatments. Scratch testing measures the load required to cause failure on the treated surface layer. This study showcases the Nanovea Tribometer and Mechanical Tester as ideal tools for evaluation and quality control of electric wires.
Test Procedure and Procedures
Coefficient of friction (COF) and wear resistance of two different surface treatments on copper wires (Wire A and Wire B) were evaluated by the Nanovea tribometer using a linear reciprocating wear module. An Al₂O₃ ball (6 mm diameter) is the counter material used in this application. The wear track was examined using Nanovea’s 3D non-contact profilometer. Test parameters are summarized in Table 1.
A smooth Al₂O₃ ball as a counter material was used as an example in this study. Any solid material with different shape and surface finish can be applied using a custom fixture to simulate the actual application situation.
Results and Discussion
Wear of copper wire:
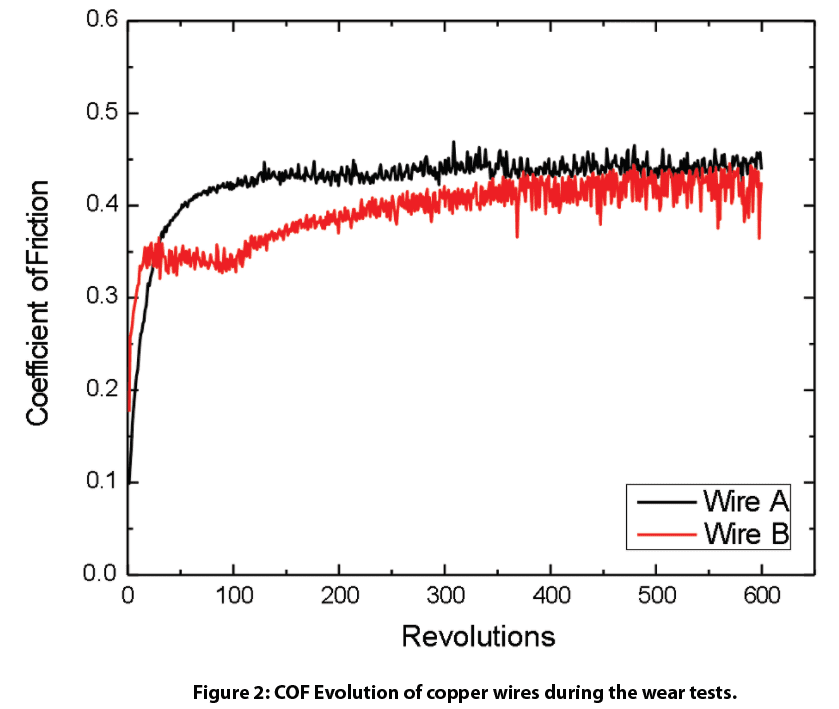
Figure 2 shows COF evolution of the copper wires during wear tests. Wire A shows a stable COF of ~0.4 throughout the wear test while wire B exhibits a COF of ~0.35 in the first 100 revolutions and progressively increases to ~0.4.
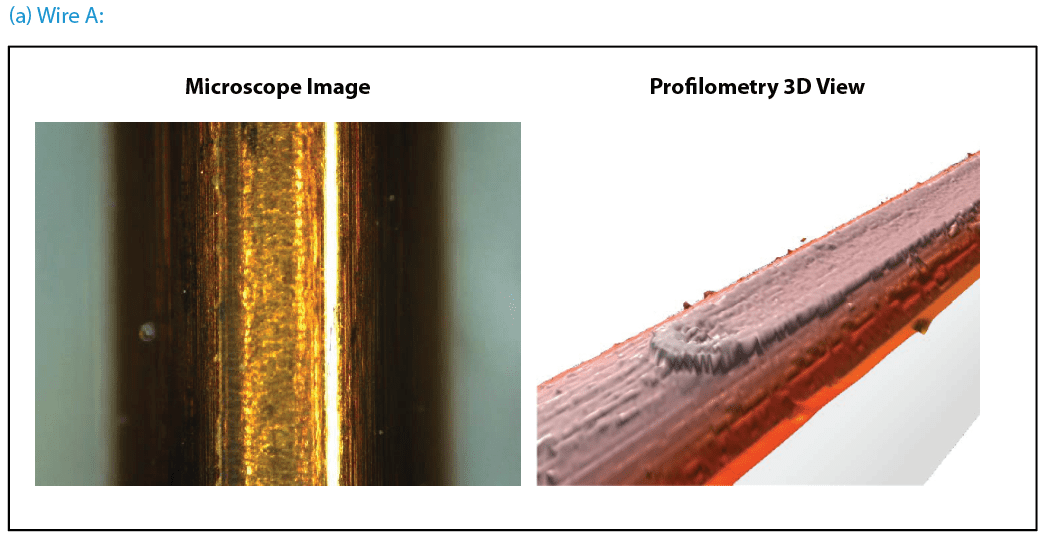
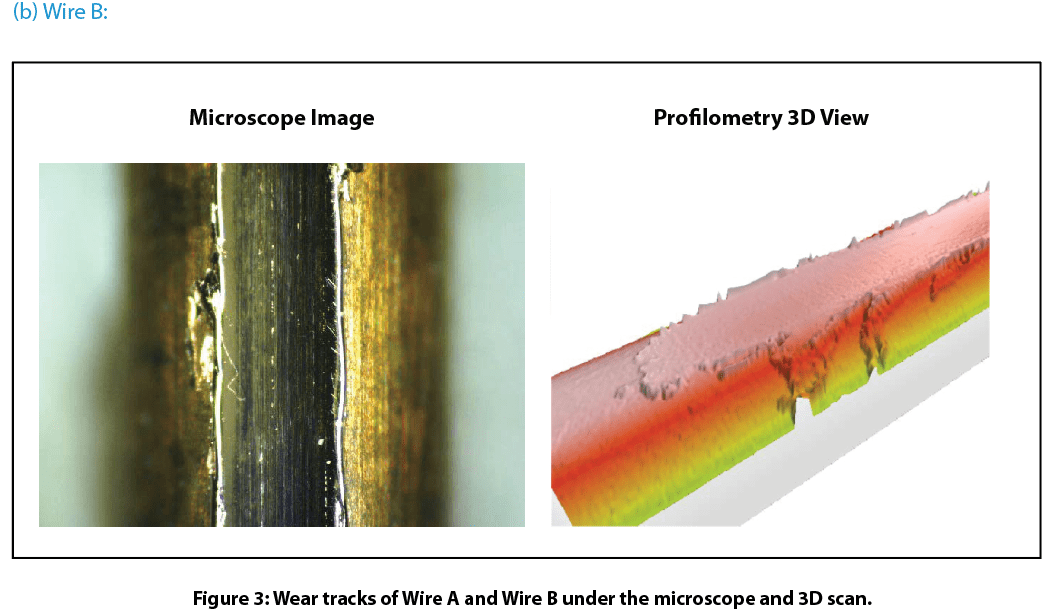
Figure 3 compares wear tracks of the copper wires after tests. Nanovea’s 3D non-contact profilometer offered superior analysis of the detailed morphology of wear tracks. It allows direct and accurate determination of the wear track volume by providing a fundamental understanding of the wear mechanism. Wire B’s surface has signi¬ficant wear track damage after a 600-revolution wear test. The profilometer 3D view shows the surface treated layer of Wire B removed completely which substantially accelerated the wear process. This left a flattened wear track on Wire B where copper substrate is exposed. This may result in significantly shortened lifespan of electrical equipment where Wire B is used. In comparison, Wire A exhibits relatively mild wear shown by a shallow wear track on the surface. The surface treated layer on Wire A did not remove like the layer on Wire B under the same conditions.
Scratch resistance of the copper wire surface:
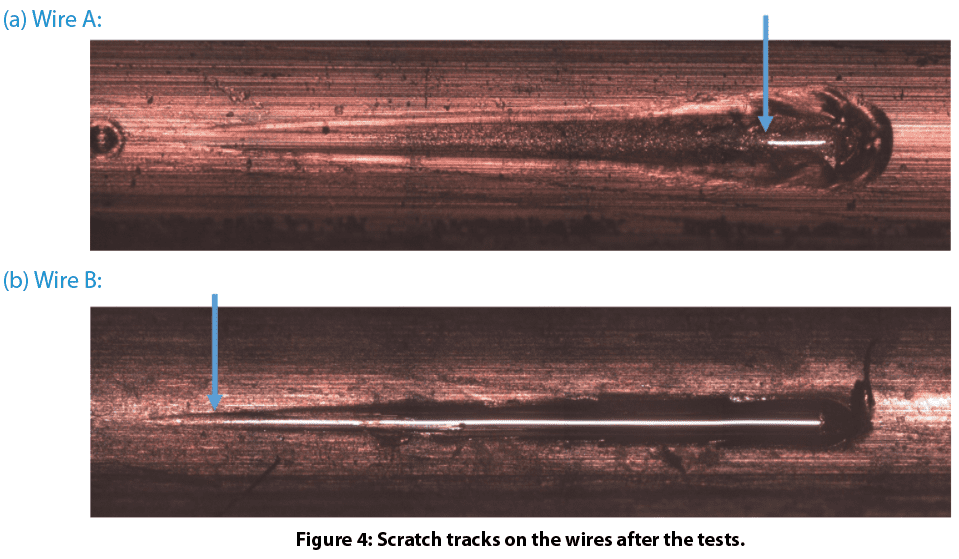
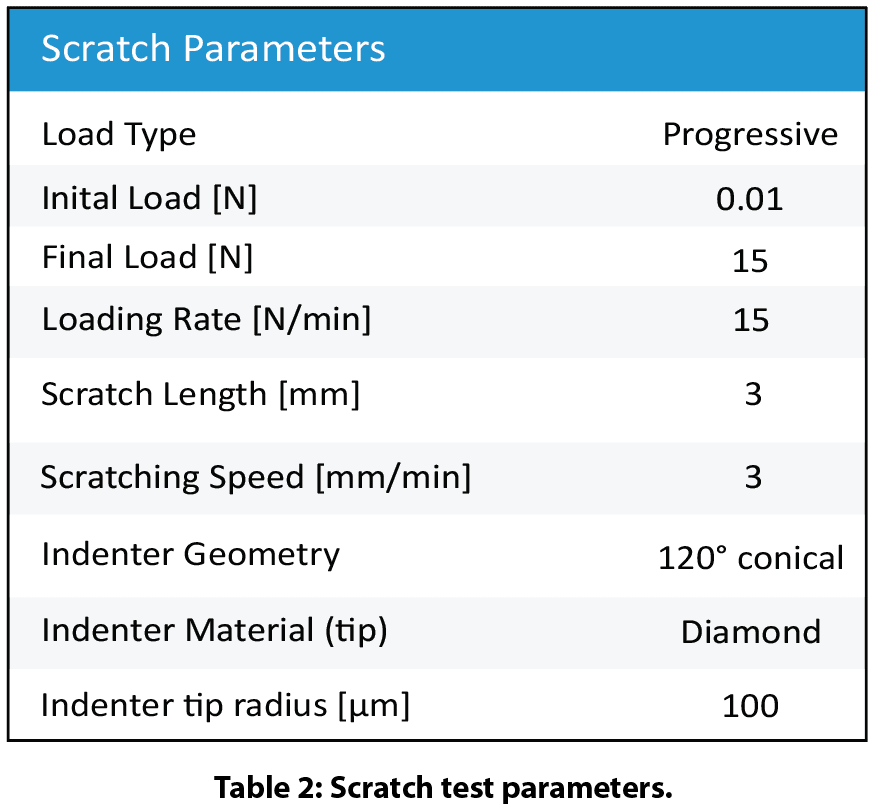
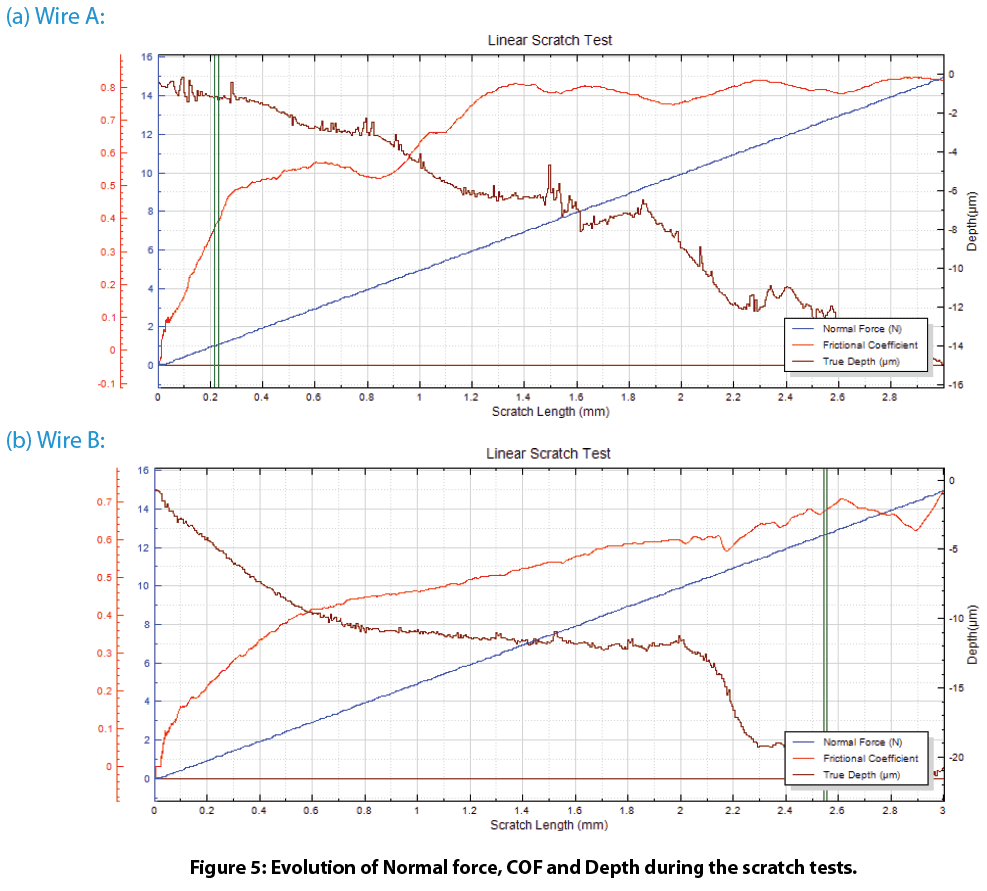
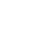
Figure 4 shows the scratch tracks on the wires after testing. The protective layer of Wire A exhibits very good scratch resistance. It delaminates at a load of ~12.6 N. In comparison, the protective layer of Wire B failed at a load of ~1.0 N. Such a significant difference in scratch resistance for these wires contributes to their wear performance, where Wire A possesses substantially enhanced wear resistance. The evolution of normal force, COF, and depth during the scratch tests shown in Fig. 5 provides more insight on coating failure during tests.
Conclusion
In this controlled study we showcased the Nanovea’s tribometer conducting quantitative evaluation of wear resistance for surface treated copper wires and Nanovea’s mechanical tester providing reliable assessment of copper wire scratch resistance. Wire surface treatment plays a critical role in the tribo-mechanical properties during their lifetime. Proper surface treatment on Wire A significantly enhanced wear and scratch resistance, critical in the performance and lifespan of electrical wires in rough environments.
Nanovea’s tribometer offers precise and repeatable wear and friction testing using ISO and ASTM compliant rotative and linear modes, with optional high temperature wear, lubrication, and tribo-corrosion modules available in one pre-integrated system. Nanovea’s unmatched range is an ideal solution for determining the full range of tribological properties of thin or thick, soft or hard coatings, films, and substrates.
Categories
- Application Notes
- Block on Ring Tribology
- Corrosion Tribology
- Friction Testing | Coefficient of Friction
- High Temperature Mechanical Testing
- High Temperature Tribology
- Humidity and Gases Tribology
- Humidity Mechanical Testing
- Indentation | Creep and Relaxation
- Indentation | Fracture Toughness
- Indentation | Hardness and Elastic
- Indentation | Loss and Storage
- Indentation | Stress vs Strain
- Indentation | Yield Strength and Fatigue
- Laboratory Testing
- Linear Tribology
- Liquid Mechanical Testing
- Liquid Tribology
- Low Temperature Tribology
- Mechanical Testing
- Press Release
- Profilometry | Flatness and Warpage
- Profilometry | Geometry and Shape
- Profilometry | Roughness and Finish
- Profilometry | Step Height and Thickness
- Profilometry | Texture and Grain
- Profilometry | Volume and Area
- Profilometry Testing
- Ring on Ring Tribology
- Rotational Tribology
- Scratch Testing | Adhesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Cohesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Multi-Pass Wear
- Scratch Testing | Scratch Hardness
- Scratch Testing Tribology
- Tribology Testing
- Uncategorized
Archives
- November 2025
- September 2023
- August 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- July 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- July 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- October 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- November 2010
- January 2010
- April 2009
- March 2009
- January 2009
- December 2008
- October 2008
- August 2007
- July 2006
- March 2006
- January 2005
- April 2004