INTRODUCTION
Sandpaper consists of abrasive particles glued to one face of a paper or cloth. Various abrasive materials can be used for the particles, such as garnet, silicon carbide, aluminum oxide and diamond. Sandpaper is widely applied in a variety of industrial sectors to create specific surface finishes on wood, metal and drywall. They often work under high pressure contact applied by hand or power tools.
IMPORTANCE OF EVALUATING SANDPAPER ABRASION PERFORMANCE
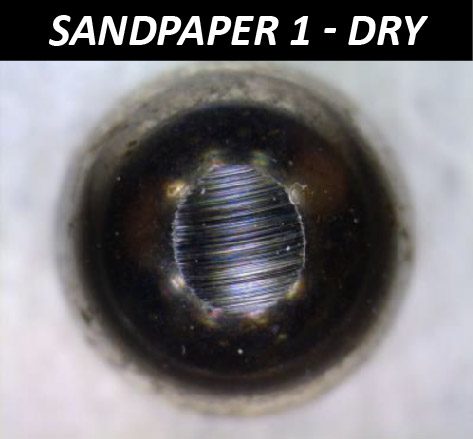
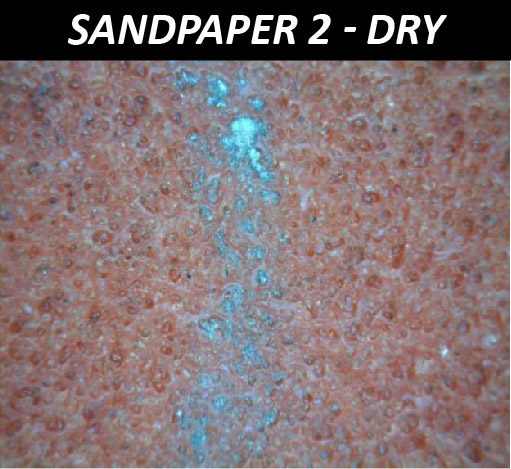
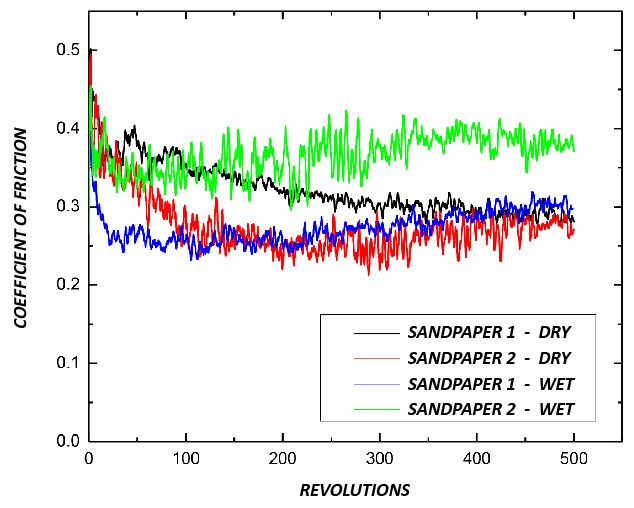
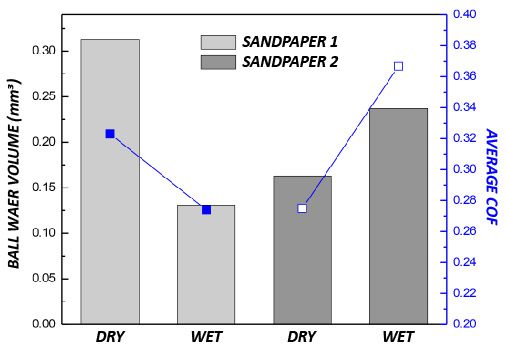
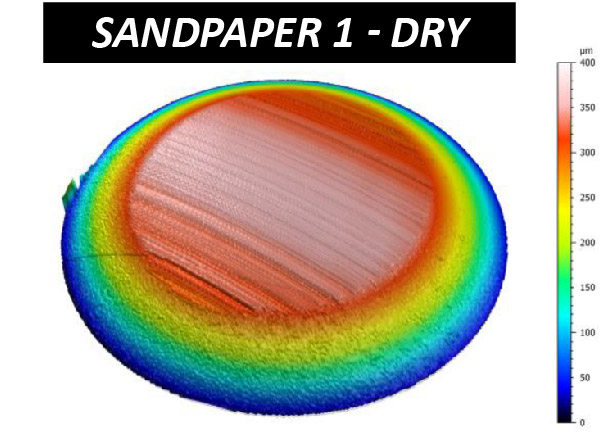
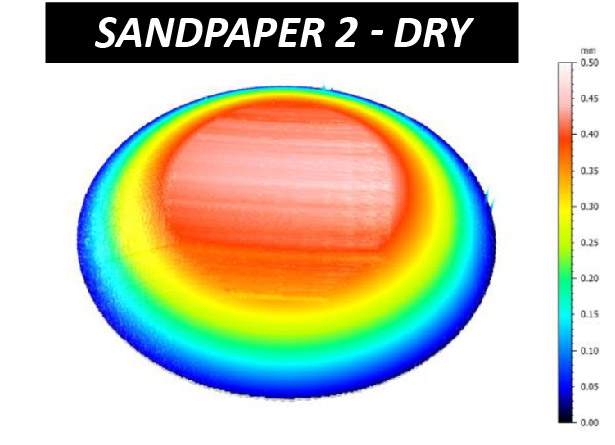
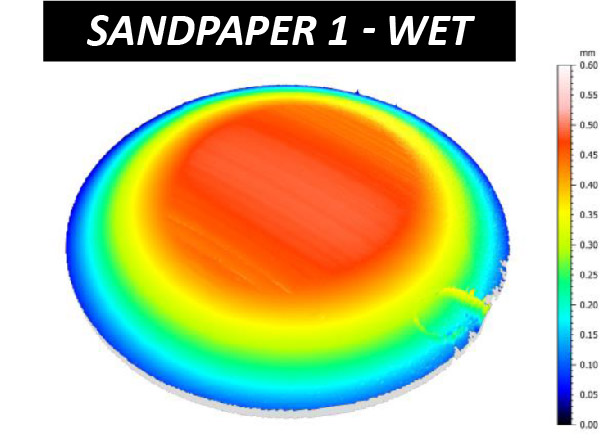
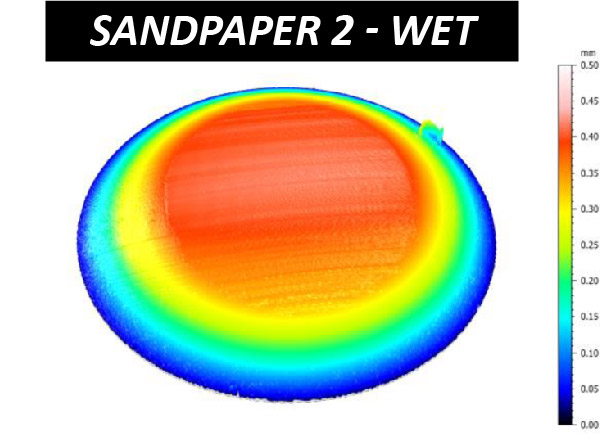
The effectiveness of sandpaper is often determined by its abrasion performance under different conditions. The grit size, i.e. the size of the abrasive particles embedded in the sandpaper, determines the wear rate and the scratch size of the material being sanded. Sandpapers of higher grit numbers have smaller particles, resulting in lower sanding speeds and finer surface finishes. Sandpapers with the same grit number but made of different materials can have unalike behaviors under dry or wet conditions. Reliable tribological evaluations are needed to ensure that manufactured sandpaper possesses the desired abrasive behavior intended. These evaluations allow users to quantitatively compare the wear behaviors of different types of sandpapers in a controlled and monitored manner in order to select the best candidate for the target application.