INTRODUCTION
Belt drive transmits power and tracks relative movement between two or more rotating shafts. As a simple and inexpensive solution with minimal maintenance, belt drives are widely used in a variety of applications, such as bucksaws, sawmills, threshers, silo blowers and conveyors. Belt drives can protect the machinery from overload as well as damp and isolate vibration.
IMPORTANCE OF WEAR EVALUATION FOR BELT DRIVES
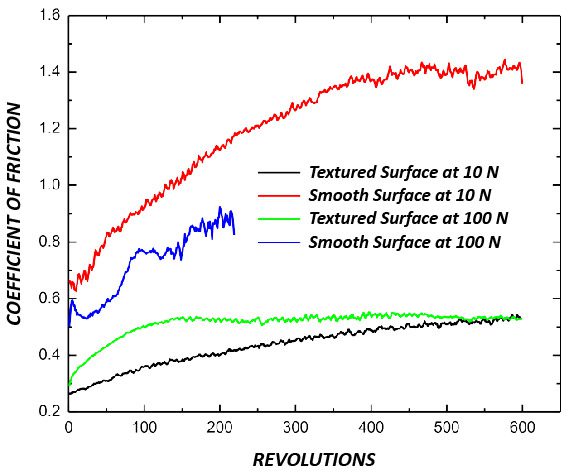
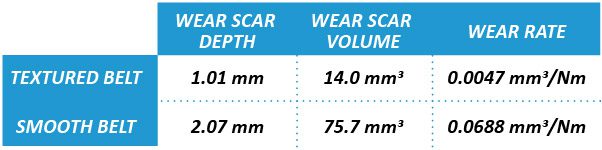
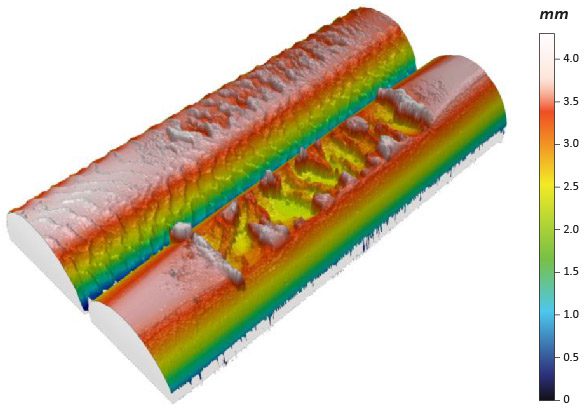
Friction and wear are inevitable for the belts in a belt-driven machine. Sufficient friction ensures effective power transmission without slipping, but excessive friction may rapidly wear the belt. Different types of wear such as fatigue, abrasion and friction take place during the belt drive operation. In order to extend the lifetime of the belt and to cut the cost and time on belt repairing and replacement, reliable evaluation of the wear performance of the belts is desirable in improving belt lifespan, production efficiency and application performance. Accurate measurement of the coefficient of friction and wear rate of the belt facilitates R&D and quality control of belt production.