Efecto de la humedad en la tribología del revestimiento de DLC
Importancia de la evaluación del desgaste del DLC en condiciones de humedad
Los recubrimientos de carbono tipo diamante (DLC) poseen propiedades tribológicas mejoradas, concretamente una excelente resistencia al desgaste y un coeficiente de fricción (COF) muy bajo. Los recubrimientos de DLC imprimen características de diamante cuando se depositan sobre distintos materiales. Las propiedades tribo-mecánicas favorables hacen que los recubrimientos de DLC sean preferibles en diversas aplicaciones industriales, como piezas aeroespaciales, hojas de afeitar, herramientas de corte de metal, cojinetes, motores de motocicletas e implantes médicos.
Los revestimientos de DLC presentan un COF muy bajo (inferior a 0,1) frente a bolas de acero en condiciones de alto vacío y en seco.12. Sin embargo, los recubrimientos de DLC son sensibles a los cambios de las condiciones ambientales, en particular a la humedad relativa (HR)3. Los entornos con alta humedad y concentración de oxígeno pueden provocar un aumento significativo del COF4. La evaluación fiable del desgaste en condiciones de humedad controlada simula las condiciones ambientales realistas de los revestimientos de DLC para aplicaciones tribológicas. Los usuarios seleccionan los mejores revestimientos de DLC para las aplicaciones deseadas mediante una comparación adecuada.
de los comportamientos de desgaste del DLC expuesto a diferentes humedades.
Objetivo de medición
Este estudio muestra la tecnología Nanovea Tribómetro equipado con un controlador de humedad es la herramienta ideal para investigar el comportamiento de desgaste de los recubrimientos de DLC a distintas humedades relativas.
Procedimiento de ensayo
La resistencia a la fricción y al desgaste de los recubrimientos de DLC se evaluó con el tribómetro Nanovea. Los parámetros de ensayo se resumen en la Tabla 1. Un controlador de humedad acoplado a la tribocámara controló con precisión la humedad relativa (HR) con una exactitud de ±1%. Las huellas de desgaste en los recubrimientos de DLC y las cicatrices de desgaste en las bolas de SiN se examinaron con un microscopio óptico después de las pruebas.
Nota: Se puede aplicar cualquier material de bola sólida para simular el rendimiento de acoplamiento de diferentes materiales en condiciones ambientales como en lubricante o alta temperatura.
Resultados y debate
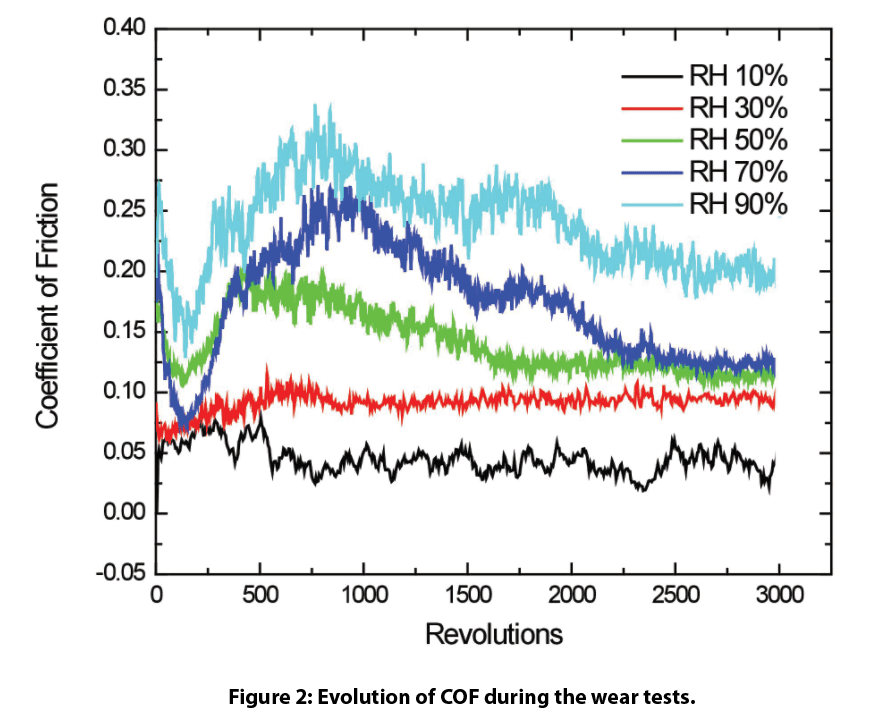
Los recubrimientos de DLC son excelentes para aplicaciones tribológicas debido a su baja fricción y a su mayor resistencia al desgaste. La fricción del recubrimiento de DLC presenta un comportamiento dependiente de la humedad, como se muestra en la figura 2. El recubrimiento de DLC muestra un COF muy bajo de ~0,05 durante todo el ensayo de desgaste en condiciones relativamente secas (10% HR). El recubrimiento de DLC muestra un COF constante de ~0,1 durante la prueba a medida que la HR aumenta hasta 30%. La fase inicial de rodaje del COF se observa en las primeras 2000 revoluciones cuando la HR aumenta por encima de 50%. El revestimiento de DLC muestra un COF máximo de ~0,20, ~0,26 y ~0,33 en HR de 50, 70 y 90%, respectivamente. Tras el periodo de rodaje, el COF del revestimiento de DLC se mantiene constante en ~0,11, 0,13 y 0,20 con HR de 50, 70 y 90%, respectivamente.
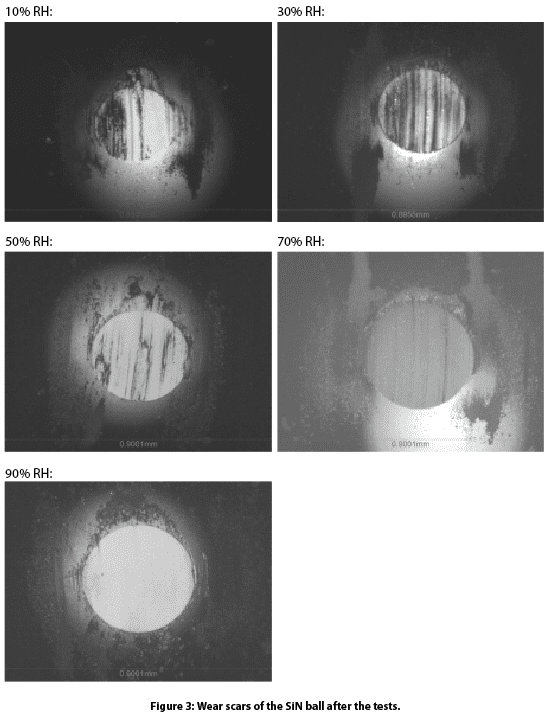
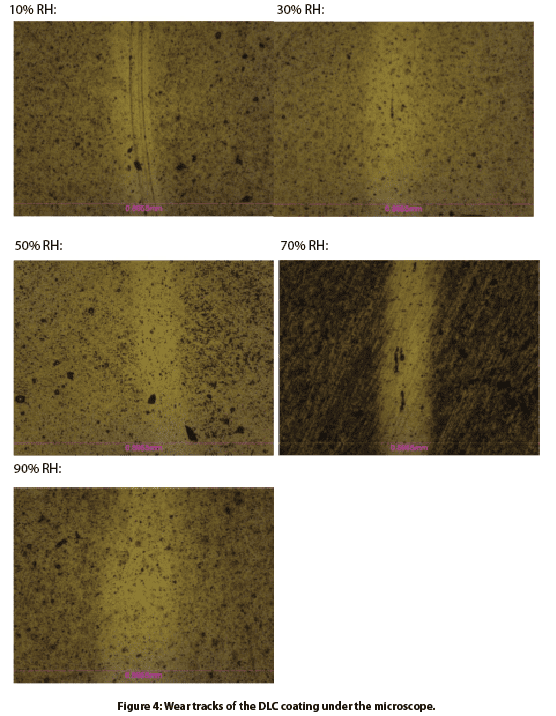
La figura 3 compara las cicatrices de desgaste de las bolas de SiN y la figura 4 compara las huellas de desgaste del recubrimiento de DLC tras las pruebas de desgaste. El diámetro de la cicatriz de desgaste era menor cuando el recubrimiento de DLC se exponía a un entorno con baja humedad. La capa de DLC transferida se acumula en la superficie de la bola de SiN durante el proceso de deslizamiento repetitivo en la superficie de contacto. En esta fase, el recubrimiento de DLC se desliza contra su propia capa de transferencia, que actúa como un lubricante eficaz para facilitar el movimiento relativo y frenar la pérdida de masa adicional causada por la deformación por cizallamiento. Se observa una película de transferencia en la cicatriz de desgaste de la bola de SiN en entornos de baja HR (por ejemplo, 10% y 30%), lo que da lugar a un proceso de desgaste desacelerado de la bola. Este proceso de desgaste se refleja en la morfología de la pista de desgaste del recubrimiento de DLC, como se muestra en la figura 4. El recubrimiento de DLC muestra una pista de desgaste más pequeña en ambientes secos, debido a la formación de una película de transferencia de DLC estable en la interfaz de contacto que reduce significativamente la fricción y la tasa de desgaste.
Conclusión
La humedad desempeña un papel fundamental en el rendimiento tribológico de los recubrimientos de DLC. El recubrimiento de DLC posee una resistencia al desgaste significativamente mejorada y una baja fricción superior en condiciones secas debido a la formación de una capa grafítica estable transferida a la contraparte deslizante (una bola de SiN en este estudio). El recubrimiento de DLC se desliza contra su propia capa de transferencia, que actúa como un lubricante eficaz para facilitar el movimiento relativo y frenar la pérdida de masa adicional causada por la deformación por cizallamiento. No se observa una película en la bola de SiN con el aumento de la humedad relativa, lo que conduce a un aumento de la tasa de desgaste en la bola de SiN y el recubrimiento de DLC.
El tribómetro Nanovea ofrece pruebas repetibles de desgaste y fricción mediante modos rotativos y lineales conformes a las normas ISO y ASTM, con módulos opcionales de humedad disponibles en un sistema preintegrado. Permite a los usuarios simular el entorno de trabajo a diferentes humedades, proporcionando a los usuarios una herramienta ideal para evaluar cuantitativamente los comportamientos tribológicos de los materiales en diferentes condiciones de trabajo.
Más información sobre el tribómetro Nanovea y el servicio de laboratorio
1 C. Donnet, Surf. Coat. Technol. 100-101 (1998) 180.
2 K. Miyoshi, B. Pohlchuck, K.W. Street, J.S. Zabinski, J.H. Sanders, A.A. Voevodin, R.L.C. Wu, Wear 225-229 (1999) 65.- K. Miyoshi.
3 R. Gilmore, R. Hauert, Surf. Coat. Technol. 133-134 (2000) 437.
4 R. Memming, H.J. Tolle, P.E. Wierenga, Thin Solid Coatings 143 (1986) 31
Categorías
- Notas de aplicación
- Bloque sobre tribología anular
- Tribología de la corrosión
- Pruebas de fricción | Coeficiente de fricción
- Pruebas mecánicas a alta temperatura
- Tribología de alta temperatura
- Humedad y gases Tribología
- Humedad Pruebas mecánicas
- Indentación | Fluencia y relajación
- Indentación | Resistencia a la fractura
- Indentación | Dureza y elasticidad
- Indentación | Pérdida y almacenamiento
- Indentación | Esfuerzo frente a deformación
- Indentación | Límite elástico y fatiga
- Pruebas de laboratorio
- Tribología lineal
- Pruebas mecánicas de líquidos
- Tribología de líquidos
- Tribología a baja temperatura
- Pruebas mecánicas
- Comunicado de prensa
- Perfilometría | Planitud y alabeo
- Perfilometría | Geometría y forma
- Perfilometría | Rugosidad y acabado
- Profilometría | Altura y grosor del escalón
- Profilometría | Textura y grano
- Perfilometría | Volumen y área
- Pruebas de perfilometría
- Tribología anillo sobre anillo
- Tribología rotacional
- Prueba de arañazos | Fallo adhesivo
- Prueba del rasguño | Fallo de cohesión
- Pruebas de arañazos | Desgaste en varias pasadas
- Pruebas de rayado | Dureza al rayado
- Pruebas de rayado Tribología
- Pruebas de tribología
- Sin categoría
Archivos
- noviembre 2025
- septiembre 2023
- agosto 2023
- junio 2023
- mayo 2023
- julio 2022
- mayo 2022
- abril 2022
- enero 2022
- diciembre 2021
- noviembre 2021
- octubre 2021
- septiembre 2021
- agosto 2021
- julio 2021
- junio 2021
- mayo 2021
- marzo 2021
- febrero 2021
- diciembre 2020
- noviembre 2020
- octubre 2020
- septiembre 2020
- julio 2020
- mayo 2020
- abril 2020
- marzo 2020
- febrero 2020
- enero 2020
- noviembre 2019
- octubre 2019
- septiembre 2019
- agosto 2019
- julio 2019
- junio 2019
- mayo 2019
- abril 2019
- marzo 2019
- enero 2019
- diciembre 2018
- noviembre 2018
- octubre 2018
- septiembre 2018
- julio 2018
- junio 2018
- abril 2018
- marzo 2018
- febrero 2018
- noviembre 2017
- octubre 2017
- septiembre 2017
- agosto 2017
- junio 2017
- mayo 2017
- marzo 2017
- febrero 2017
- enero 2017
- noviembre 2016
- octubre 2016
- agosto 2016
- julio 2016
- junio 2016
- mayo 2016
- abril 2016
- marzo 2016
- febrero 2016
- enero 2016
- diciembre 2015
- noviembre 2015
- octubre 2015
- septiembre 2015
- agosto 2015
- julio 2015
- junio 2015
- mayo 2015
- abril 2015
- marzo 2015
- febrero 2015
- enero 2015
- noviembre 2014
- octubre 2014
- septiembre 2014
- agosto 2014
- julio 2014
- junio 2014
- mayo 2014
- abril 2014
- marzo 2014
- febrero 2014
- enero 2014
- diciembre 2013
- noviembre 2013
- octubre 2013
- septiembre 2013
- agosto 2013
- julio 2013
- junio 2013
- mayo 2013
- abril 2013
- marzo 2013
- febrero 2013
- enero 2013
- diciembre 2012
- noviembre 2012
- octubre 2012
- septiembre 2012
- agosto 2012
- julio 2012
- junio 2012
- mayo 2012
- abril 2012
- marzo 2012
- febrero 2012
- enero 2012
- diciembre 2011
- noviembre 2011
- octubre 2011
- septiembre 2011
- agosto 2011
- julio 2011
- junio 2011
- mayo 2011
- noviembre 2010
- enero 2010
- abril 2009
- marzo 2009
- enero 2009
- diciembre 2008
- octubre 2008
- agosto 2007
- julio 2006
- marzo 2006
- enero 2005
- abril 2004