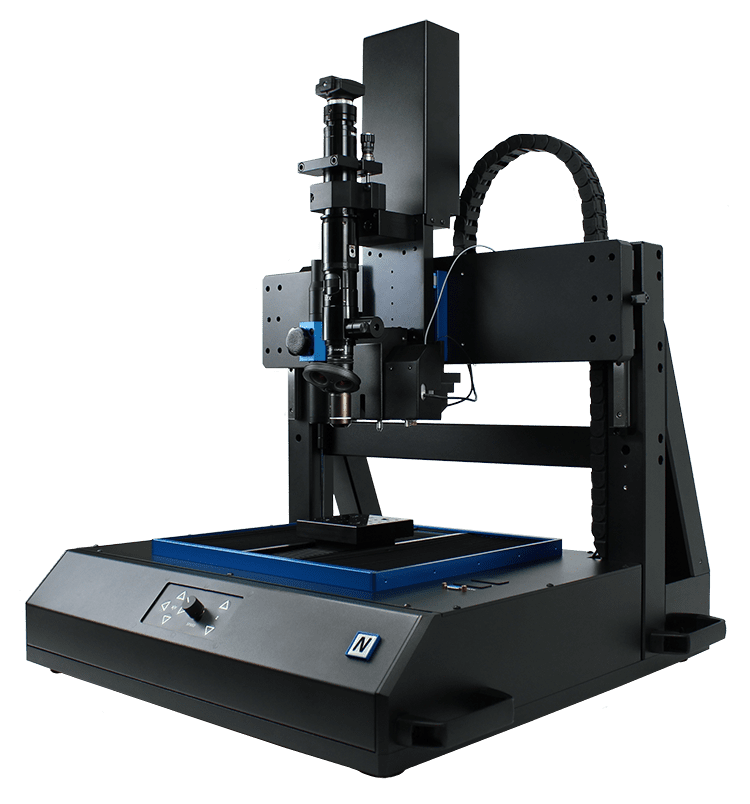
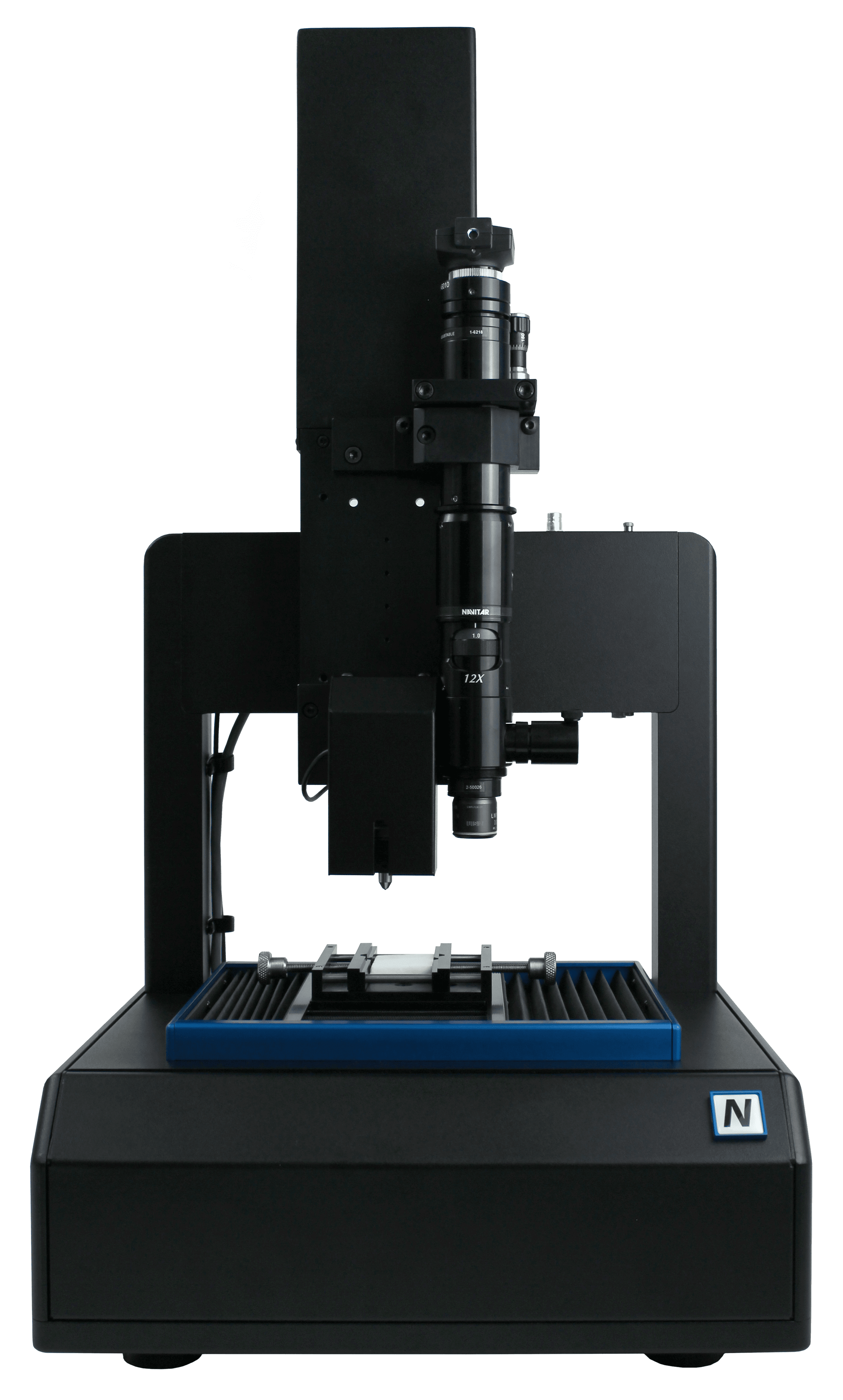
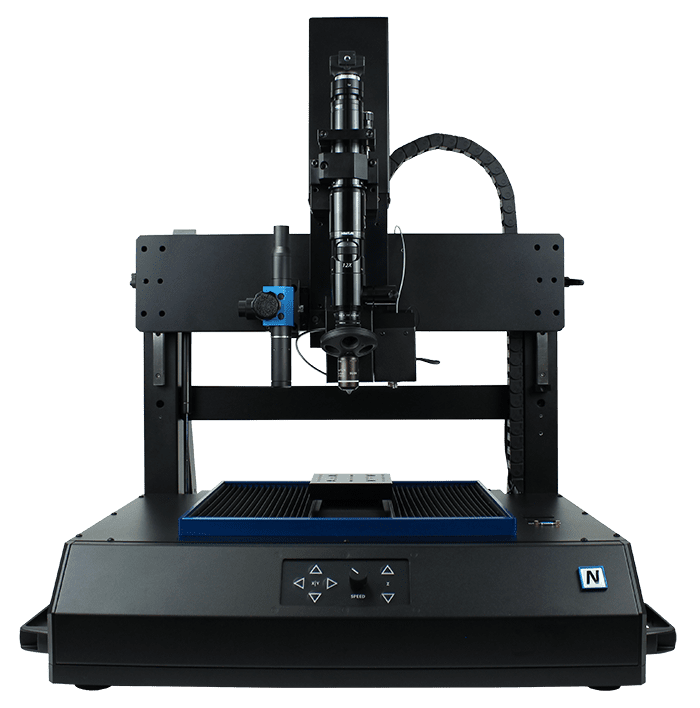
Microindentación
OVERVIEW OF MICROINDENTATION
Microindentation is a powerful analytical technique that is frequently used in material science and engineering to quantify the mechanical properties of a variety of materials. It is a non-destructive method of measurement, which involves the use of a sharp, pointed probe to indent the surface of a sample material, with the force applied being carefully controlled. The resulting indentation is then measured to assess the material’s hardness, elastic modulus, and other mechanical properties. The technique has enabled scientists to better understand the mechanical behavior of a wide variety of materials, from metals and ceramics to polymers and composites. Whether you are studying the microstructure of materials or developing new materials with specific properties, microindentation is a valuable tool that can help you gain insights into a material’s mechanical behavior.
Índice
¿Tienes preguntas?
Limitaciones de las pruebas de indentación tradicionales
Indentation tests are commonly used to evaluate material properties, but traditional methods have their limitations. One of the key drawbacks is these tests often cannot accurately capture microscale deformations and can be influenced by surface roughness and other surface irregularities. This is where microindentation tests offer a more advanced solution. By using a much smaller indenter and specialized equipment, researchers can analyze microscopic regions of a material with greater accuracy. Additionally, microindentation allows for more flexibility in testing different types of samples, such as thin films or materials with complex surface geometries. While traditional tests still play an important role in material characterization, microindentation is becoming increasingly popular for precise, efficient analysis.
Advantages of Microindentation Testing
Microindentation is a valuable analytical method that allows researchers to measure the mechanical properties of materials with a high degree of precision. By applying a small, controlled force to the surface of a material and measuring the resulting indentation depth, scientists can gain insight into a material’s hardness, elastic modulus, fracture toughness, yield strength, and fatigue. One of its significant advantages is the ability to test materials under different environmental conditions such as high or low temperature, liquid immersion, or humidity/vacuum exposure. Another key advantage of microindentation is its versatility—it can be used to analyze a wide range of materials, from metals and ceramics to polymers and biological tissues. Additionally, microindentation testing is non-destructive, meaning that it can be performed on small or delicate samples without causing damage. These benefits make microindentation an essential tool for researchers across numerous scientific fields, from materials science and engineering to biomedicine and beyond. In the field of material science, microindentation testing is a crucial process that provides valuable insights into the mechanical properties of materials.
DISCOVER MICROINDENTATION TESTING
CON LOS ENSAYADORES MECÁNICOS DE NANOVEA
NANOVEA Microindentation Software Features
- Recetas
- Exportar datos sin procesar e imágenes
- Visualización en tiempo real
- Informes automáticos
- Soporte multilingüe
- Compare curvas y resultados en muestras iguales o múltiples
NANOVEA Advanced Microindentation Automation
- FastMap: Mapeo de dureza y módulo de elasticidad (3 segundos por indentación)
- Herramienta de selección de mapas Broadview: Cartografía avanzada en imágenes unidas
- Prueba automatizada de múltiples muestras (admite variaciones de altura de hasta 50 mm).
- Navegación Plus: imágenes de navegación de superficie fáciles de usar
- Enfoque rápido, detección automática de superficies y análisis automático
- Herramientas de calibración fácil y directa para carga y profundidad
- Función de área de sangría única (Patente europea n.º 3076153)
- Control de calidad cuantificable para penetrador (Patente europea n.º 3076153)
- Asistente (patente en trámite): generador automático de parámetros de prueba.
- Recetas guardables de todos los macros programados
Normas
Nanovea realiza pruebas de rayado de conformidad con las normas establecidas, lo que garantiza resultados precisos y confiables para evaluar las propiedades mecánicas de los materiales, al tiempo que ofrece soluciones de prueba personalizadas diseñadas para aplicaciones únicas.
- ASTM E384: Método de prueba estándar para la dureza por microindentación de materiales.
- ASTM G171: Método de prueba estándar para determinar la dureza al rayado de materiales utilizando una punta de diamante.
- ASTM E2546: Práctica estándar para ensayos de indentación instrumentados.
- ASTM B933: Método de prueba estándar para la dureza por microindentación de materiales de pulvimetalurgia (PM).
- ASTM D4065: Práctica estándar para plásticos: Propiedades mecánicas dinámicas: Determinación e informe de procedimientos.
- ISO 14577 – Materiales metálicos. Ensayo de indentación instrumentado para determinar la dureza y los parámetros de los materiales.
- DIN 50359: Ensayo universal de dureza de materiales metálicos. Calibración de bloques de referencia.


Simulación de condiciones reales
Alta y baja temperatura, líquido, humedad y vacío
TEMPERATURA ALTA
TEMPERATURA BAJA
LÍQUIDO
HUMEDAD
VACÍO
By subjecting materials to simulated environmental conditions, we can better understand how they will perform in real-world applications, helping us to design more durable and reliable products. Whether it is for aerospace, automotive, or other industries, microindentation testing is an essential component in ensuring that materials can stand up to the rigors of their intended use. Overall, the importance of microindentation testing in environmental conditions cannot be overstated, and plays a critical role in materials science research.
Measurement and Analysis Techniques in Microindentation
Microindentation is a widely used technique in materials engineering to measure mechanical properties like hardness, modulus of elasticity, and fracture toughness at the microscale level. There are several advanced techniques and equipment available for the measurement and analysis of microindentation data with high precision and accuracy. Some of the popular techniques include load-displacement curves, optical microscopy, finite element analysis, and machine learning algorithms. These techniques provide insights into the deformation behavior of materials and the underlying physics of the microindentation process. Additionally, the data generated by these techniques can be used to study the structure-property relationships of materials and aid in the development of new materials with tailored mechanical properties. Overall, the measurement and analysis techniques in microindentation have significant implications across various industrial and academic fields.
Dureza y módulo de elasticidad
In microindentation testing, hardness and elastic modulus are two fundamental properties that are accurately measured by pressing a sharp indenter into a surface of a material. Hardness is derived from the material’s resistance to permanent deformation under the indenter’s load, and is an important indication of the material’s ability to resist wear and tear. Elastic modulus, on the other hand, measures how much a material deforms under load and how well it springs back when the load is removed. Understanding these two parameters can provide valuable insights into the mechanical behavior and performance of a material at the microscale level, which is essential for many fields ranging from material science to engineering.
Resistencia a la fractura
Fracture toughness is a measure of the resistance of a material against crack propagation and is a fundamental property of material degradation, especially in applications where loading occurs over a wide range. Microindentation-based fracture toughness measurements are particularly useful in assessing the strength of brittle materials, such as ceramics and composites, which are prone to failure under stress. The fracture toughness measurement obtained through microindentation testing is a critical factor that contributes to the efficiency and safety of products in various applications, including electronics, aerospace, energy, and biomedical fields.
Límite elástico y fatiga
Yield strength and fatigue are two critical material properties that can be evaluated using microindentation techniques. Yield strength is the stress level at which a material begins to deform plastically, causing permanent changes to its structure. Fatigue, on the other hand, refers to the weakening of a material over time due to repetitive loading and unloading cycles. Microindentation testing can also be used to measure the fatigue resistance of materials, making it a valuable tool for predicting the longevity of structures in various settings.
Fluencia y relajación
Creep refers to the time-dependent deformation of a material under a constant load or stress, while relaxation is the time-dependent decrease in stress or load required to maintain a given level of deformation. These phenomena are influenced by several factors such as temperature, strain rate, and the microstructural features of the material. Understanding creep and relaxation behavior is essential for predicting the durability and reliability of materials used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
Medición de tensión y deformación
Stress and strain refer to the amount of deformation a material undergoes under different loads, and measuring these variables is crucial to the design of materials that withstand mechanical stress. By analyzing the force required to create a specified indentation depth, it is possible to determine a wide range of mechanical properties of the material. Microindentation testing is particularly useful for materials that are too small or too thin to be tested using traditional mechanical testing methods. Today, this technique is widely used in fields such as materials science, biomechanics, and microelectronics to better understand the behavior of materials at the microscale.
Tipos de penetradores

Microindentation testing is a useful tool for researchers who want to measure the mechanical properties of small materials. By using different types of indenters, scientists can accurately determine the hardness and other properties of materials. Vickers and Berkovich indenters are commonly used to measure hardness and elastic modulus in various hard and soft materials. Vickers indenters are more resistant at higher loads, while Berkovich indenters offer more sensitivity for measuring thinner coatings. Cube corner indenters are useful for measuring fracture toughness at lower forces, while conico-spherical indenters are used for softer metals and plastics materials. The elongated Knoop indenter is useful for measuring directional differences in hardness for materials with fibers. Flat indenters are ideal for crushing small particles or measuring ultimate yield strength in various materials. Special knife diamond indenters are useful for testing failure in cylindrical parts like fiber optics. Each type of indenter has unique features, and researchers must choose the right one for their specific application to obtain accurate and precise data. Microindentation testing is a powerful method that can provide valuable analytical data for research purposes, enabling more precise measurements of material mechanical properties
Conclusión
Microindentation is a powerful and versatile technique that enables the measurement of various properties of materials such as hardness, elastic modulus, fracture toughness, and yield strength. The accuracy of results from microindentation, however, relies heavily on the selection of appropriate testing equipment, measurement techniques and analysis methods to achieve reliable results. Overall, microindentation has significant applications in engineering and material science that adds to our understanding of the mechanical behavior of materials. If you are interested in learning more about how this technique can be utilized for your particular application needs, reach out to our team today to chat with a knowledgeable representative. Our experienced staff will be able to answer all your questions and discuss product options specific to your requirements. Don’t wait any longer – contact us now!