Surface Roughness and Features of a Solar Cell
Importance of Solar Panel Testing
Maximizing a solar cell’s energy absorption is key for the technology’s survival as a renewable resource. The multiple layers of coating and glass protection allow for the absorption, transmittance, and reflection of light that is necessary for the photovoltaic cells to function. Given that most consumer solar cells operate at 15-18% efficiency, optimizing their energy output is an ongoing battle.
Studies have shown that surface roughness plays a pivotal role in the reflectance of light. The initial layer of glass must be as smooth as possible to mitigate the reflectance of light, but the subsequent layers do not follow this guideline. A degree of roughness is necessary at each coatings interface to another to increase the possibility of light scattering within their respective depletion zones and increase the absorption of light within the cell1. Optimizing the surface roughness in these regions allows the solar cell to operate to the best of its ability and with the Nanovea HS2000 High Speed Sensor, measuring surface roughness can be done quickly and accurately.
Measurement Objective
In this study we will display the capabilities of the Nanovea Profilometer HS2000 with High Speed Sensor by measuring the surface roughness and geometric features of a photovoltaic cell. For this demonstration a monocrystalline solar cell with no glass protection will be measured but the methodology can be used for various other applications.
Test Procedure and Procedures
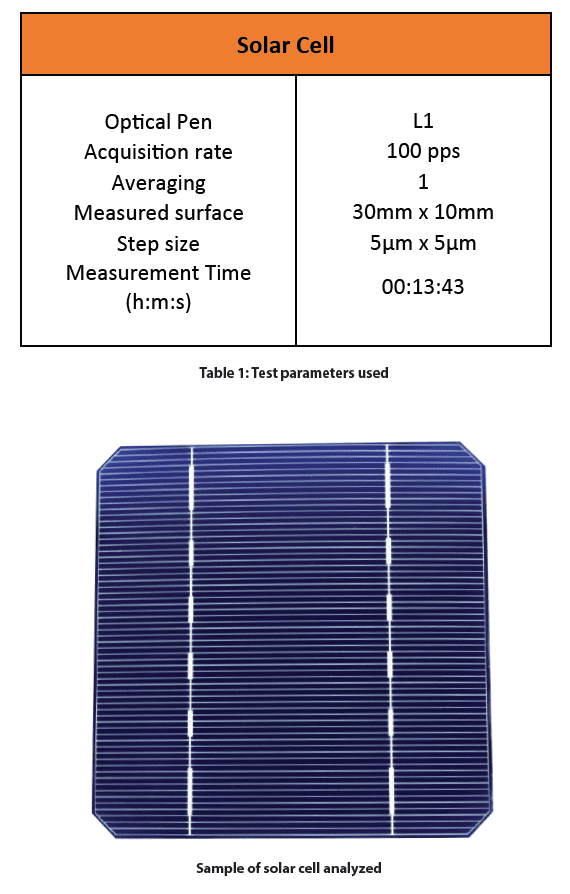
The following test parameters were used to measure the surface of the solar cell.
Results and Discussion
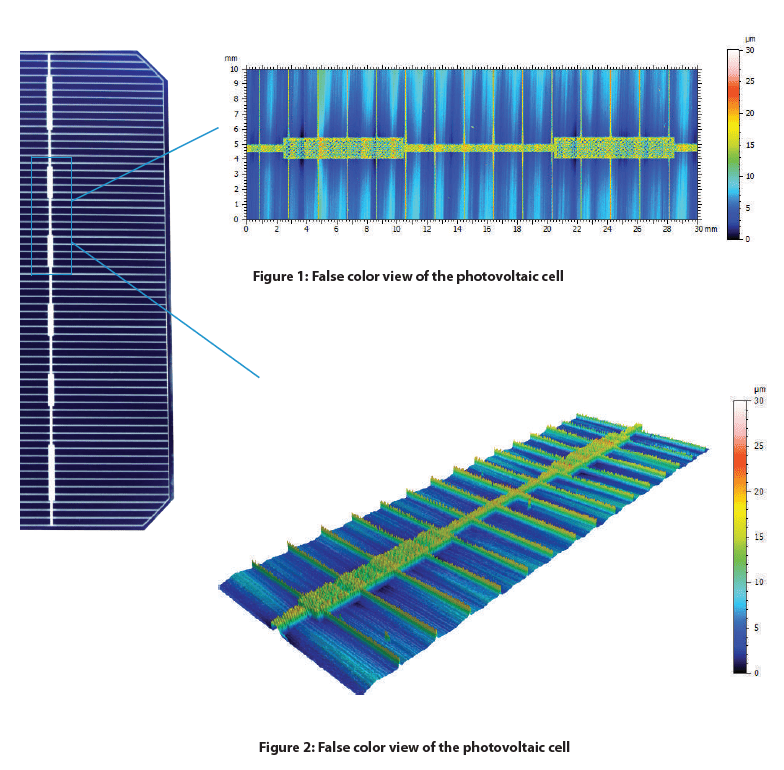
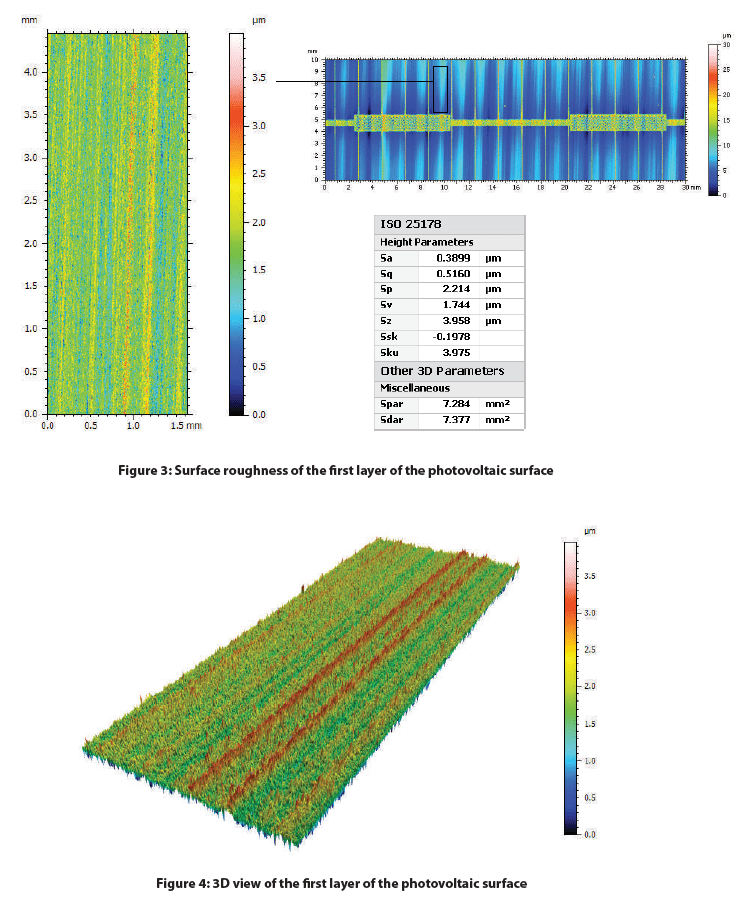
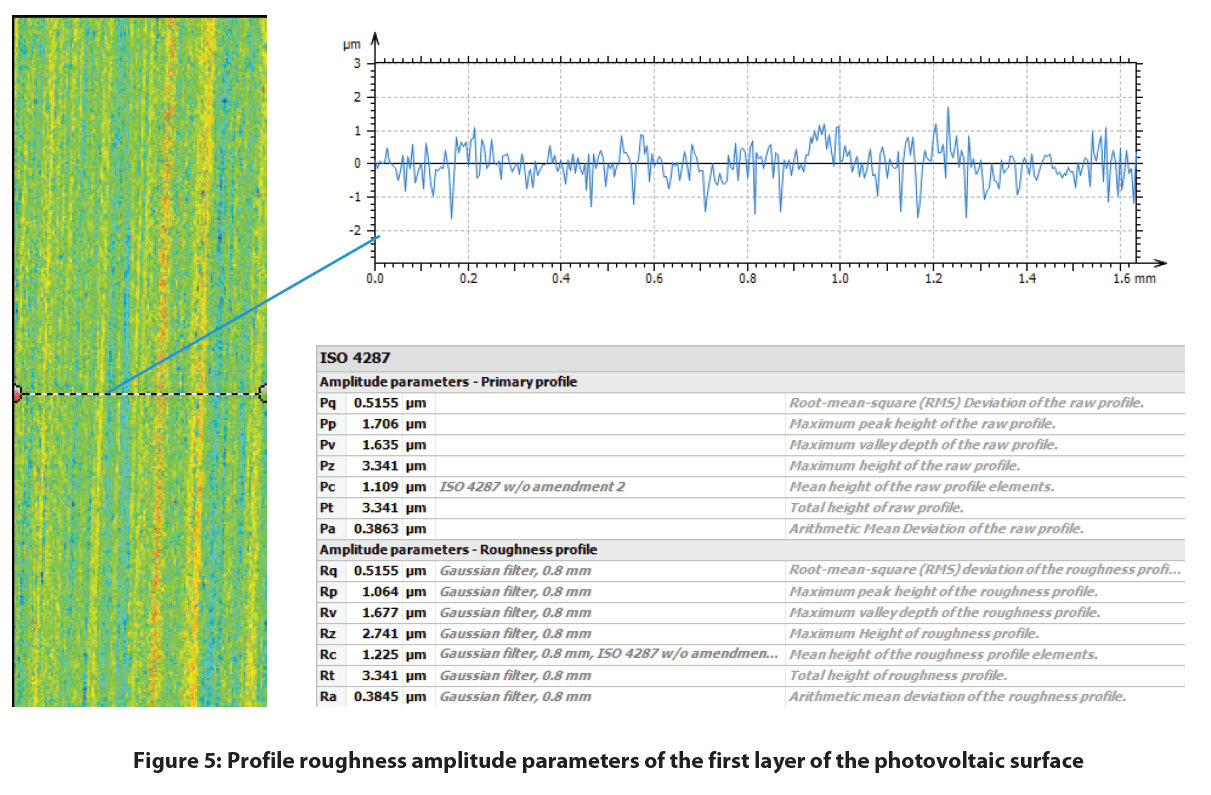
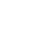
Depicted below is the 2D false-color view of the solar cell and an area extraction of the surface with its respective height parameters. A Gaussian filter was applied to both surfaces and a more aggressive index was used to flatten the extracted area. This excludes form (or waviness) larger than the cut-off index, leaving behind features that represent the solar cell’s roughness.
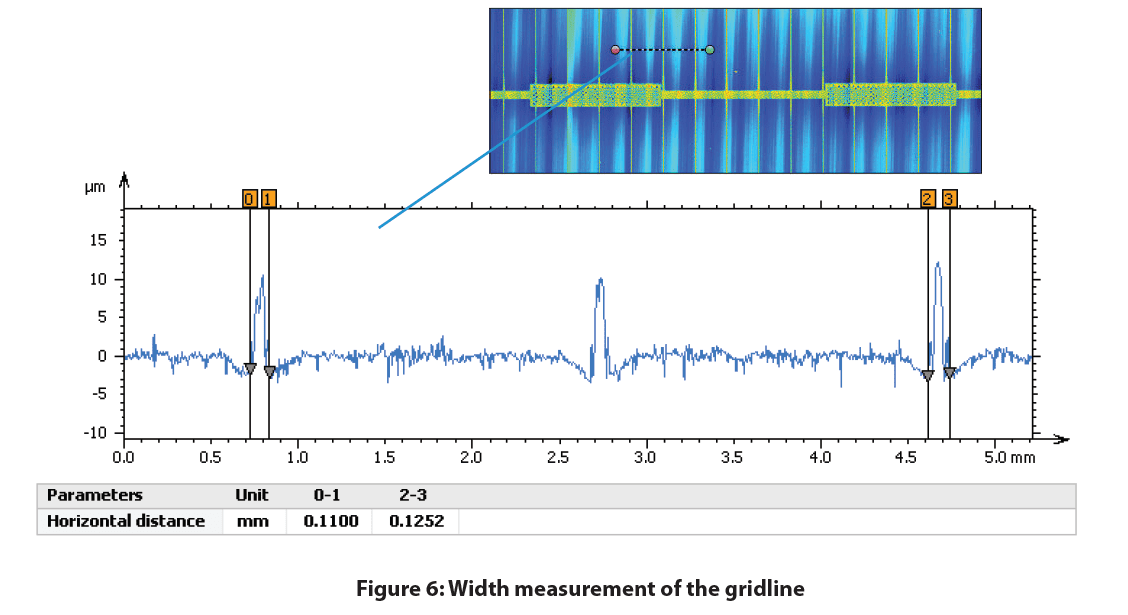
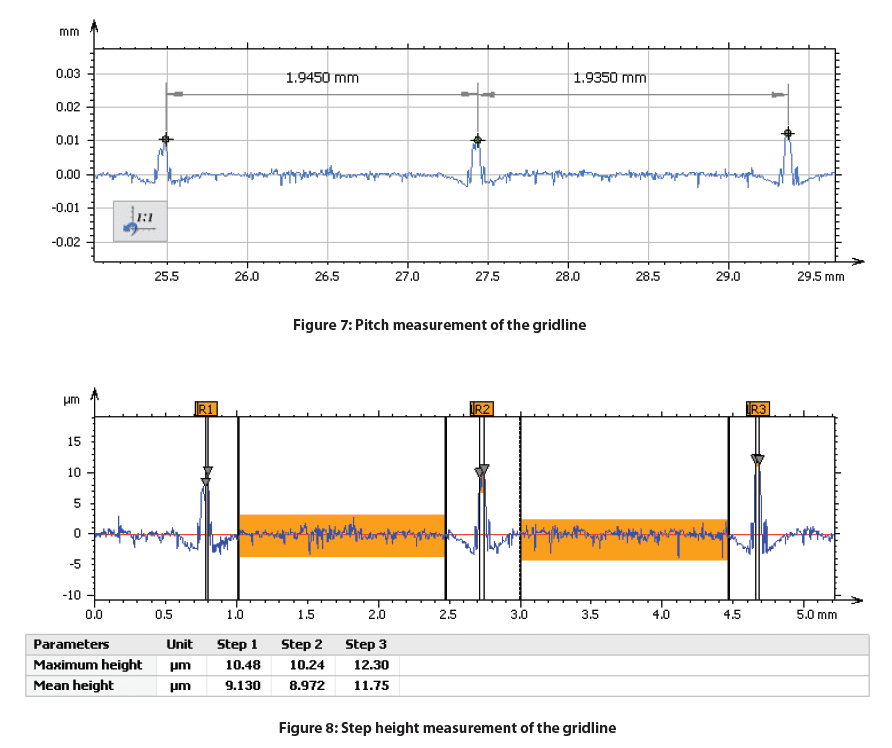
Conclusion

In this study we were able to display the Nanovea HS2000 Line Sensor’s ability to measure a monocrystalline photovoltaic cell’s surface roughness and features. With the ability to automate accurate measurements of multiple samples and set pass fail limits, the Nanovea HS2000 Line Sensor is a perfect choice for quality control inspections.
Reference
1 Scholtz, Lubomir. Ladanyi, Libor. Mullerova, Jarmila. “Influence of Surface Roughness on Optical Characteristics of Multilayer Solar Cells “ Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, vol. 12, no. 6, 2014, pp. 631-638.
NOW, LET'S TALK ABOUT YOUR APPLICATION
Categorías
- Application Notes
- Block on Ring Tribology
- Corrosion Tribology
- Friction Testing | Coefficient of Friction
- High Temperature Mechanical Testing
- High Temperature Tribology
- Humidity and Gases Tribology
- Humidity Mechanical Testing
- Indentation | Creep and Relaxation
- Indentation | Fracture Toughness
- Indentation | Hardness and Elastic
- Indentation | Loss and Storage
- Indentation | Stress vs Strain
- Indentation | Yield Strength and Fatigue
- Laboratory Testing
- Linear Tribology
- Liquid Mechanical Testing
- Liquid Tribology
- Low Temperature Tribology
- Mechanical Testing
- Press Release
- Profilometry | Flatness and Warpage
- Profilometry | Geometry and Shape
- Profilometry | Roughness and Finish
- Profilometry | Step Height and Thickness
- Profilometry | Texture and Grain
- Profilometry | Volume and Area
- Profilometry Testing
- Ring on Ring Tribology
- Rotational Tribology
- Scratch Testing | Adhesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Cohesive Failure
- Scratch Testing | Multi-Pass Wear
- Scratch Testing | Scratch Hardness
- Scratch Testing Tribology
- Tradeshow
- Tribology Testing
- Uncategorized
Archivos
- septiembre 2023
- agosto 2023
- junio 2023
- mayo 2023
- julio 2022
- mayo 2022
- abril 2022
- enero 2022
- diciembre 2021
- noviembre 2021
- octubre 2021
- septiembre 2021
- agosto 2021
- julio 2021
- junio 2021
- mayo 2021
- marzo 2021
- febrero 2021
- diciembre 2020
- noviembre 2020
- octubre 2020
- septiembre 2020
- julio 2020
- mayo 2020
- abril 2020
- marzo 2020
- febrero 2020
- enero 2020
- noviembre 2019
- octubre 2019
- septiembre 2019
- agosto 2019
- julio 2019
- junio 2019
- mayo 2019
- abril 2019
- marzo 2019
- enero 2019
- diciembre 2018
- noviembre 2018
- octubre 2018
- septiembre 2018
- julio 2018
- junio 2018
- mayo 2018
- abril 2018
- marzo 2018
- febrero 2018
- noviembre 2017
- octubre 2017
- septiembre 2017
- agosto 2017
- junio 2017
- mayo 2017
- abril 2017
- marzo 2017
- febrero 2017
- enero 2017
- noviembre 2016
- octubre 2016
- agosto 2016
- julio 2016
- junio 2016
- mayo 2016
- abril 2016
- marzo 2016
- febrero 2016
- enero 2016
- diciembre 2015
- noviembre 2015
- octubre 2015
- septiembre 2015
- agosto 2015
- julio 2015
- junio 2015
- mayo 2015
- abril 2015
- marzo 2015
- febrero 2015
- enero 2015
- noviembre 2014
- octubre 2014
- septiembre 2014
- agosto 2014
- julio 2014
- junio 2014
- mayo 2014
- abril 2014
- marzo 2014
- febrero 2014
- enero 2014
- diciembre 2013
- noviembre 2013
- octubre 2013
- septiembre 2013
- agosto 2013
- julio 2013
- junio 2013
- mayo 2013
- abril 2013
- marzo 2013
- febrero 2013
- enero 2013
- diciembre 2012
- noviembre 2012
- octubre 2012
- septiembre 2012
- agosto 2012
- julio 2012
- junio 2012
- mayo 2012
- abril 2012
- marzo 2012
- febrero 2012
- enero 2012
- diciembre 2011
- noviembre 2011
- octubre 2011
- septiembre 2011
- agosto 2011
- julio 2011
- junio 2011
- mayo 2011
- noviembre 2010
- enero 2010
- abril 2009
- marzo 2009
- enero 2009
- diciembre 2008
- octubre 2008
- agosto 2007
- julio 2006
- marzo 2006
- enero 2005
- abril 2004